Customer Satisfaction Improvement: The Kano Analysis Method
Understanding the determinants of customer satisfaction is critical for organizations that want to produce products and services that meet or exceed the expectations of their customers. Customer satisfaction is a key component of any successful business. A powerful method that helps companies identify and prioritize the characteristics and attributes that drive customer satisfaction is called Kano Analysis. This article introduces Kano Analysis and explains how it can be used to analyze customer satisfaction.
What is Kano Analysis?
Definition and History
It was created in the 1980s by Dr. Noriaki Kano, a Japanese professor of quality management. Kano Analysis seeks to comprehend consumer preferences and determine which product characteristics or traits are most significant to consumers.
While employed at the Tokyo University of Science in the late 1970s, Dr. Noriaki Kano started his studies on customer satisfaction. He was looking for a methodical method for figuring out how to transform client demands and expectations into product features.
According to BABOK, Kano Analysis is “a technique for understanding which product features will help drive customer satisfaction”.
The finding that customers' satisfaction with particular product features was not entirely based on their existence or absence served as the inspiration for Kano's study. He understood that the extent to which certain features are fulfilled affects consumer satisfaction and that the absence of particular features may even make customers less satisfied.
Goals and Opportunities
Understanding customer wants, ranking product or service features, and eventually increasing customer satisfaction are the main goals of Kano analysis. Organizations may learn important lessons about what consumers really want and how to satisfy their expectations by using this analysis method.
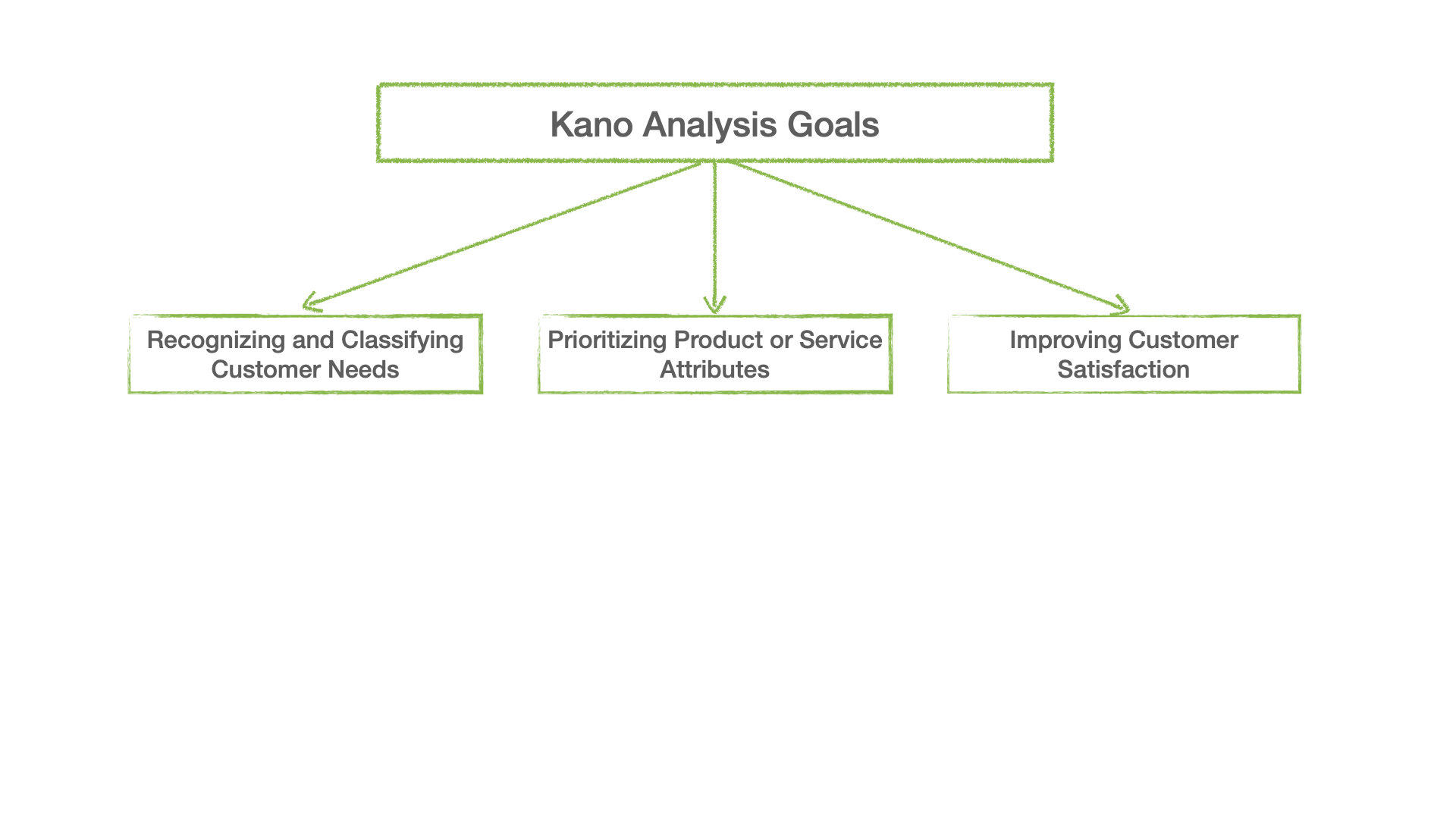
Recognizing and classifying customer needs. Kano Analysis offers a thorough insight of what customers deem necessary, desirable, or even unexpected in a good or service by helping to discover and categorize several sorts of customer demands. By classifying demands into distinct groupings, it goes beyond conventional surveys or feedback systems and enables businesses to deploy resources more wisely.
Prioritizing product or service attributes. The capacity of Kano Analysis to prioritize attributes depending on client preferences is one of its main advantages. Organizations may distinguish between fundamental, performance, and exciting features by classifying consumer demands according to the Kano Model's numerous dimensions. Companies may concentrate their efforts and resources on the areas that will have the greatest impact on customer satisfaction attributable to this prioritizing.
Improving customer satisfaction. Organizations may adjust their solutions to meet or exceed expectations by knowing the many kinds of the customer wants. Organizations may create a strong foundation for customer satisfaction by effectively addressing fundamental demands and performance characteristics. Additionally, adding elements of excitement may deliver unexpected surprises that go above and beyond what customers expect, resulting in greater loyalty and favorable word-of-mouth.
Enhanced product development, higher market competitiveness, and improved consumer loyalty are all advantages of applying Kano Analysis. By utilizing this type of analysis approach, businesses may match their products and services to the preferences of their customers, resulting in long-term success and enduring growth.
Read also: Backlogs in Achieving Development Goals: from Product Vision to Release
Concepts: Satisfaction and Functionality
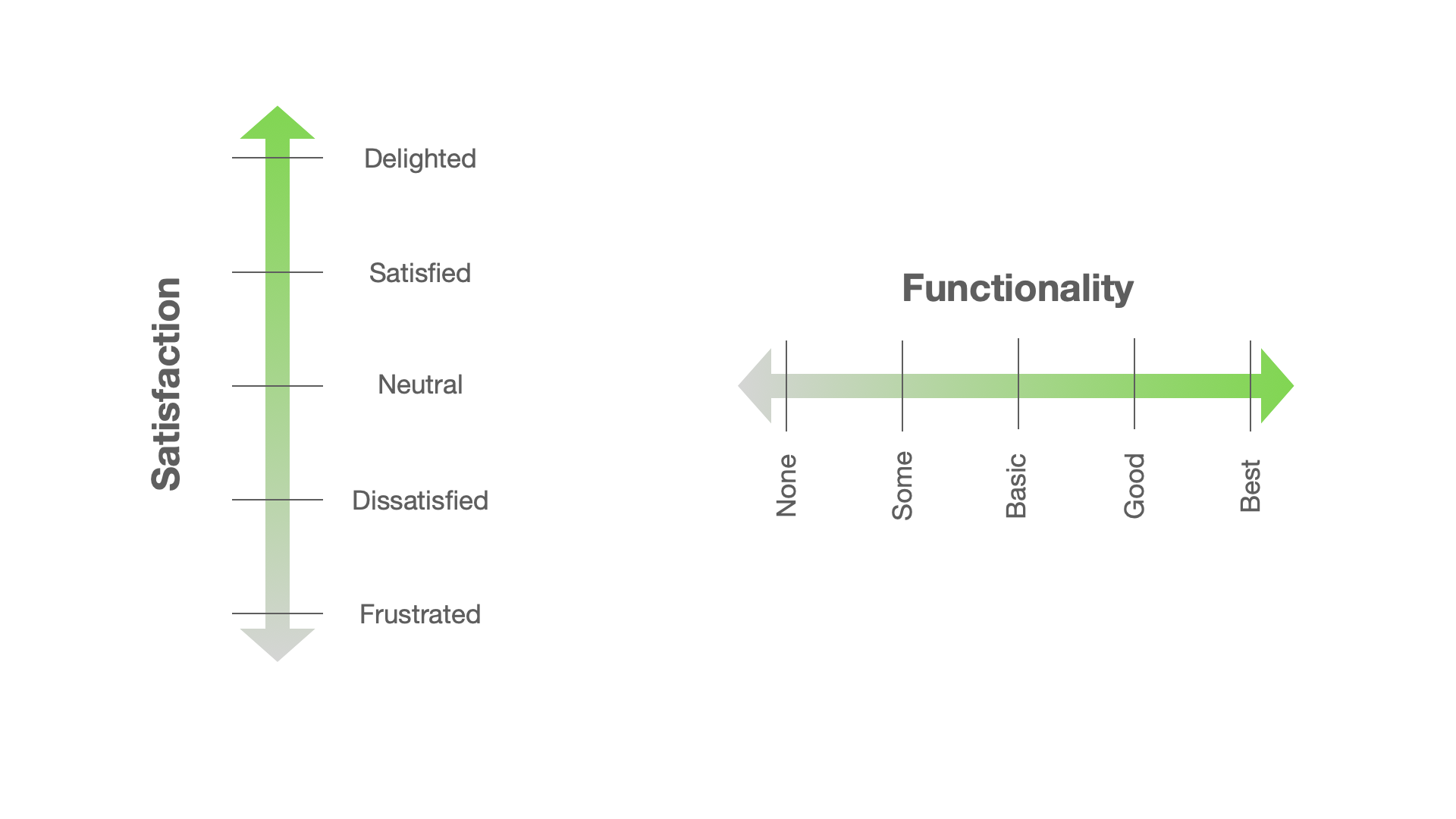
Kano Analysis uses two key concepts - satisfaction and functionality - to analyze customer needs and preferences. It classifies different types of customer criteria based on how they affect customer satisfaction. The study helps prioritize features and functions that have the greatest impact on customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Functionality. The basic features and capabilities of a product or service are referred to as its functionality. These are the basic qualities that customers demand and often take for granted. Functionality is the basic standard that must be met for a product or service to be evaluated. Customers and functionality often follow a straight line, so as functionality increases, so does customer satisfaction. However, greater than expected functionality does not always translate into greater enjoyment.
Satisfaction. Kano Analysis defines satisfaction as the customer's emotional response to the presence or absence of a particular product or service attribute. It measures the degree to which a product or service meets the consumer's needs and expectations. Both the functional and non-functional characteristics of a product affect customer satisfaction.
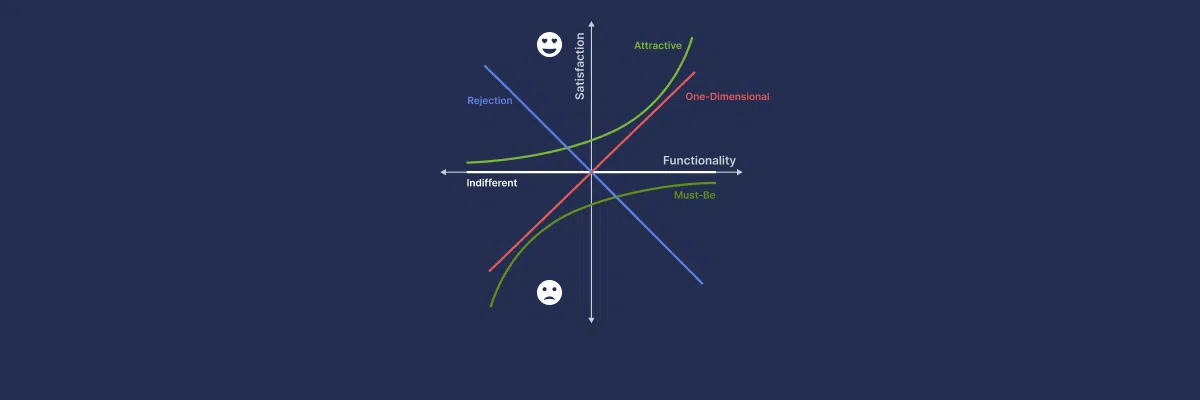
The Five Customer Preference Categories
In order to comprehend the link between client preferences and product attributes, the Kano Analysis approach is utilized in product development and customer satisfaction studies. It divides these characteristics into five different categories: Must-Be (or Must-Have, or Basic), One-Dimensional (or Linear, or Performance), Attractive (or Delighters), Indifferent, and Reverse attributes. Let's go into each category and examine its traits, instances, and implications.
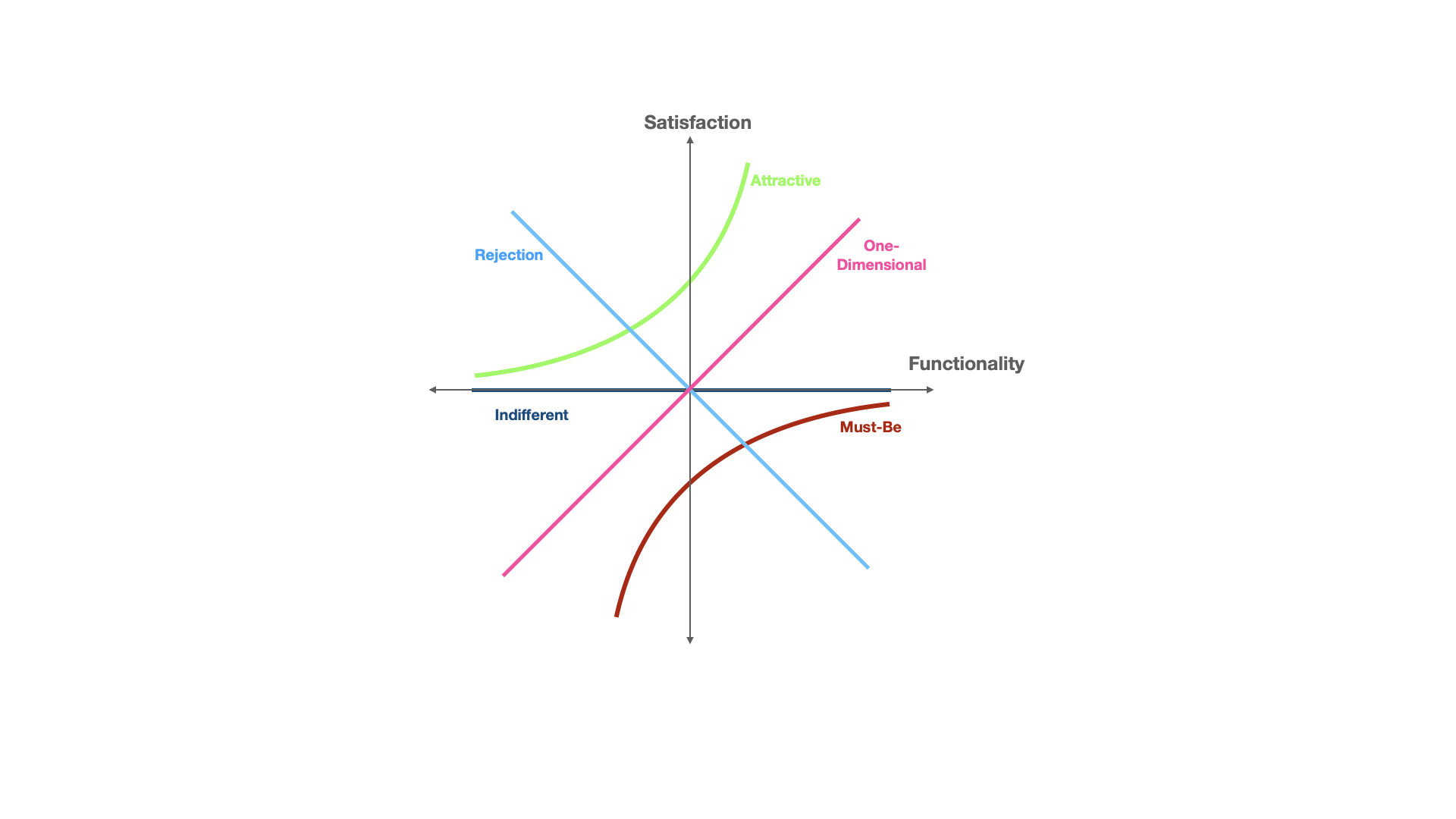
Must-Be Attributes
Must-Be attributes are the basic features or qualities that customers consider necessary in the product or service. They are the requirements that must be met in order for customers to be satisfied. However, meeting these basic requirements does not guarantee customer satisfaction or loyalty. Must-Be attributes focus on preventing dissatisfaction rather than promoting it.
For example, customers expect their laptops to have a usable keyboard, a reliable battery, and enough storage space. Although these features are essential, customers do not see them as providing value beyond their basic needs.
One-Dimensional Attributes
When satisfied, one-dimensional attributes are closely correlated with customer satisfaction. The degree to which these attributes are met or exceeded determines customer satisfaction, which is linearly related. Customers are more likely to remain loyal when expectations in this area are met or exceeded.
The speed of an Internet connection is an example of a one-dimensional characteristic. If a customer's expectations are met or exceeded, they are satisfied. Customers have specific performance expectations. Dissatisfaction results when the Internet connection isn't as fast as they want it to be.
Attractive Attributes
Customers may not explicitly expect Attractive attributes, but when they do, they can create pleasant surprises and joy. These qualities go beyond what the consumer expects and create a memorable experience. They have the ability to differentiate a product or service in a competitive marketplace.
A hotel that offers complimentary spa services or a vehicle with a built-in massage feature are two examples of enticing qualities. Customers are delighted and more likely to become brand loyalists when they encounter these unexpected attributes.
Indifferent Attributes
Customer satisfaction is not significantly affected by indifferent attributes. Customers do not care about or expect these attributes. They are considered neutral elements that do not significantly affect the overall customer experience.
The color of a pen is an example of an indifferent attribute. The majority of consumers do not care what color pen they use, while others may have a preference. As a result, spending money to offer a variety of pen colors may not have much impact on customer loyalty or satisfaction.
Reverse Attributes
Reverse attributes are features or characteristics that, when present, can make customers dissatisfied. The impact of these attributes on customer satisfaction and loyalty is disproportionately negative. To stop customer churn and bad word-of-mouth, it is essential to identify and address negative attributes.
Customers are likely to be disappointed and may choose to dine elsewhere if, for example, a restaurant frequently provides delayed service or offers cuisine that is below acceptable quality standards. The restaurant's reputation can suffer as a result of these unfavorable incidents, and repeat business can be lost.
Kano Analysis helps product development teams prioritize their efforts and focus on the features that will have the greatest impact on customer satisfaction by classifying customer requirements into these different groups. It enables organizations to identify essential requirements, deal with one-dimensional requirements, and even include appealing elements that may go beyond what customers would expect.
It's crucial to remember one fundamental truth: categories are dynamic and change over time. Customers' perceptions of a particular product feature today may not be indicative of how they will feel later.
Read also: Feature Prioritization Techniques for Your MVP
How to Conduct a Kano Analysis
A survey based on the Kano analysis approach is quick and easy to conduct. For each feature, a functional question and a dysfunctional question are posed, both with the same possible answers:
What do you think about the inclusion of feature Y in product X / service X?
What do you think about product X / service X not having feature Y / not having feature Y?
Kano Analysis Process
The following is a process to build a Kano Model.
- Define the goal. The goal of the Kano Analysis should be made very clear. Define your goals and the specific product, service, or feature you want to evaluate.
- Obtain customer attributes. Decide on the most important characteristics or aspects of the item or service you want to study. These characteristics should have a direct effect on customer satisfaction. Make a list of these attributes or characteristics.
- Establish a customer survey. Create a survey questionnaire with questions about each characteristic or aspect identified in the previous step. The survey should gather customer comments and thoughts about these characteristics.
- Conduct the survey. Send the survey to the audience you want to reach. Responses can be collected using a variety of techniques, including online surveys, email, in-person interviews, and focus groups. Make sure the sample you have is representative of your target market.
- Gather and evaluate data. Collect survey responses, then compile the information. Analyze the data for patterns and trends. Sort the responses into the following categories for each attribute, as discussed in the previous section.
- Dysfunctional
Delighted
Satisfied
Neutral
Dissatisfied
Frustrated
Functional
Delighted
Q
A
A
A
O
Satisfied
R
Q
I
I
M
Neutral
R
I
I
I
M
Dissatisfied
R
I
I
Q
M
Frustrated
R
R
R
R
Q
Example of responses categorization, where M - Must-Be attribute, O - One-Dimensional attribute, A - Attractive attribute, I - Indifferent attribute, R - Reverse attribute, Q - Questionable
- Create the Kano model. Make a Kano Model based on the analysis from the previous step. Place each characteristic in the appropriate category on the model. Customer satisfaction and the presence of the characteristic are the two axes that make up the Kano Model.
- Prioritize your steps. Review the Kano Model and prioritize your actions according to the results. Focus your attention on improving or incorporating qualities that fall into the "One-Dimensional" and "Must-Be" zones. These are the attributes that can have a big impact on customer satisfaction and give you an edge.
- Share results and put changes into practice. Communicate the results of the Kano Analysis to the organization's stakeholders. Describe the results, highlight the areas that need improvement, and suggest some next actions. Implement the necessary changes to improve customer satisfaction and your product or service based on the prioritized activities.
Keep in mind that a Kano analysis is an iterative process. To stay on top of consumer expectations and maintain a competitive edge, it's critical to revisit the analysis frequently as market dynamics and customer preferences change.
Case: Healthcare Management System
Let's look at an example of performing a Kano analysis on a healthcare IT management system.
- The goal of this Kano analysis is to assess the capabilities and qualities of a healthcare IT management system in order to understand user satisfaction and identify the most pressing issues for development.
- Using a healthcare IT management system as an example, consider the following key attributes:
- User experience and usability
- Access management and security
- Data storage and management
- Integration with other systems
- Reporting and analysis capabilities
- Process automation
- Scalability and efficiency
- Resources for help and training - Create a survey questionnaire with questions for each attribute. Below are some sample questions for each attribute:
- User experience and usability.
Functional: How satisfied are you with the user interface of the healthcare IT management system?
Dysfunctional: How frustrated are you with the complexity and challenge of the user interface?
- Access management and security.
Functional: How confident are you that the system can control user access and protect critical data?
Dysfunctional: How concerned are you that the system is vulnerable to security breaches and illegal access?
- Data storage and management.
Functional: In terms of the management and storage of your data, how satisfied are you with the system?
Dysfunctional: How often does the system experience problems with data loss or corruption?
- Integration with other systems.
Functional: How effectively does your healthcare organization's IT management system interface with other platforms?
Dysfunctional: How annoying is it when a system's attempts to interface with other systems fail, resulting in inconsistent data and disrupted workflows?
- Reporting and analysis capabilities.
Functional: How satisfied are you with the reporting and analysis capabilities of the IT management system?
Dysfunctional: Given the system's shortcomings, how much time and effort does it take you to produce accurate and insightful reports?
- Process automation.
Functional: To what extent does your healthcare organization's system automate and simplify workflows?
Dysfunctional: How often do errors or bottlenecks cause delays and inefficiencies in workflow automation processes?
- Scalability and efficiency.
Functional: How satisfied are you with the system's ability to handle increasing data volumes and user demands?
Dysfunctional: How bothered are you by system stalls or breakdowns when demand spikes during peak hours?
- Resources for help and training.
Functional: How effective are the training and support tools provided for the IT management system?
Dysfunctional: How dissatisfied are you with the response time and level of expertise of technical support when you encounter system problems? - Distribute the survey to a representative sample of healthcare managers and IT administrators who use the healthcare IT management system. Use email, targeted mailings, or online survey tools to obtain responses. Strive to get enough responses to ensure statistical validity.
- Collect survey responses, then review the information. Sort the responses into the Kano model's Must-Be, One-Dimensional, Attractive, and Indifferent categories.
According to the survey replies, you could discover, for instance:
- User experience and usability. Belongs to the category of "One-Dimensional" objects. Higher user satisfaction is the result of an easy-to-use interface.
- Access management and security. Belongs to the "Must-Be" group. Users are disappointed when there isn't enough access control and security because they expect it.
- Data storage and management. Belongs to the category of "One-Dimensional" objects. The ability to effectively manage and store data has a direct impact on customer satisfaction.
- Integration with other systems. Belongs to the "One-Dimensional" category. A critical need for customer satisfaction is seamless connectivity to other systems.
- Reporting and analysis capabilities. Falls into the "Attractive" category. Although tempting, robust reporting and analysis capabilities may not be the most important consideration.
- Process automation. Falls into the "Attractive" category. Although tempting, automated workflows may not be the primary consideration.
- Scalability and efficiency. Belongs to the category of "One-Dimensional" objects. User satisfaction is strongly influenced by the ability to scale and operate adequately under conditions of growing data volumes and user demands.
- Resources for help and training. Belongs to the "One-Dimensional" category. Higher user satisfaction is directly influenced by efficient training and support resources. - Plot each characteristic on the Kano Model according to its category in light of the study.
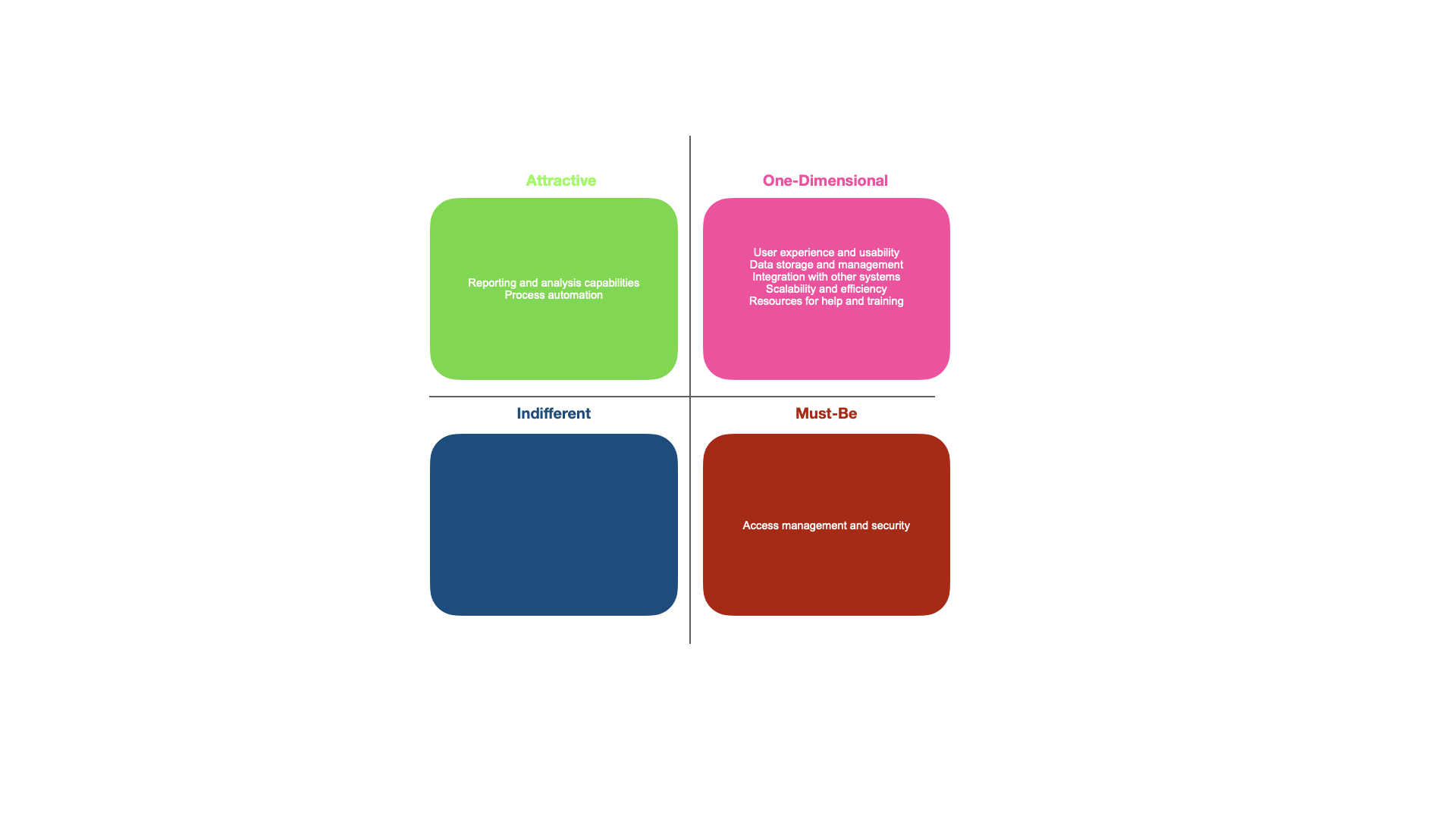
- Review the Kano Model and then prioritize your to-do list based on the results. Focus on improving or adding features in the "One-Dimensional" and "Attractive" categories. For example, user satisfaction can be greatly affected by improving the user interface and usability, strengthening access control and security measures, and expanding integration capabilities.
Inform the organization's stakeholders of the results of the Kano analysis. Present the results, identify areas for improvement, and propose a course of action. Implement the necessary adjustments based on the prioritized activities to increase user satisfaction and strengthen the healthcare IT management system.
Limitations and Precautions
In any case, Kano Analysis has its own limitations and difficulties that need to be taken into account, just like any other approach. In order to fully understand and adapt to changing preferences, it is also essential to combine Kano Analysis with other consumer research techniques, and to maintain ongoing customer input. Let's explore these ideas further:
- Kano Analysis classifies customer preferences into five categories. While this simplicity is helpful for initial research, it could not fully represent the complexity of customer demands and expectations. Customer tastes often fluctuate between these categories or change over time.
- Kano Analysis centers on capturing consumer preferences based on specific product attributes or features. It ignores factors such as customer demographics, market dynamics, and the state of the competitive marketplace. When evaluating the results of Kano Analysis, it is important to take these elements into account.
- Applying Kano Analysis to measurable characteristics or aspects that can be directly observed or quantified yields the best results. It may not be as beneficial for intangible factors such as emotions, brand impression or overall user experience. To overcome this limitation, Kano Analysis can be used in conjunction with other research techniques.
- It takes a lot of thought to interpret the results of Kano Analysis. A one-size-fits-all strategy may not be acceptable because different customers may have different tastes. To develop a deep understanding of customer preferences, a thorough investigation from many angles is required.
In order to overcome these limitations and to ensure in-depth knowledge, it is advisable to combine Kano Analysis with other customer research techniques.
Adapting to changing consumer preferences and maintaining customer satisfaction requires regular customer input. Organizations must be agile to respond to changing preferences and market conditions.
In summary, Kano Analysis is a useful method for identifying customer preferences and increasing customer satisfaction. Companies can prioritize their efforts and focus on the aspects that have the greatest impact on customer loyalty by grouping product attributes into different categories. However, it is critical to understand that consumer preferences are dynamic and change over time, requiring constant review of the study to adapt to changing consumer demands. While Kano Analysis provides helpful insights, it should be combined with other research methods to provide a complete picture of customer behavior.
Software Development Hub has extensive experience in creating web applications and mobile applications for healthcare businesses. When working on a project, our team takes into account the business challenges the client faces and offers safe, efficient solutions to automate processes and scale your operations while reducing costs.
Our portfolio includes medical information systems, e-Prescription systems, applications for tracking medicines with a QR scanner, medical ERP systems, etc.
Categories
About the author
Share
Need a project estimate?
Drop us a line, and we provide you with a qualified consultation.