Requirements Elicitation Techniques
One of the key concepts of software development is to bring ideas of clients or product owners into fully functional high-quality IT product. Before development begins, business analysts throw the ‘bridge’ which sets the level of communication and mutual understanding between customers and developers needed to solve the project's tasks. Requirements collecting, which includes identifying of sources, organizing of process, analyzing of stakeholders, their interaction and business-process they perform, — is the important basis stage for future software development artifacts.
Identifying of Source
Communication with stakeholders as a primary source of information needs deep understanding of the role and significance of influence level on making and approving of decisions. From this point of view Mendelow’s Model (Matrix) is a convenient tool to solve this issue.
According to this model, all stakeholders can be classified depending on two variables — their interests and their power:
- The power of stakeholders determines their ability to influence the organization.
- The interest of stakeholders is determined by their desire to influence the organization.
Therefore, the stakeholder scheme is: Stakeholder Influence = Power x Interest.
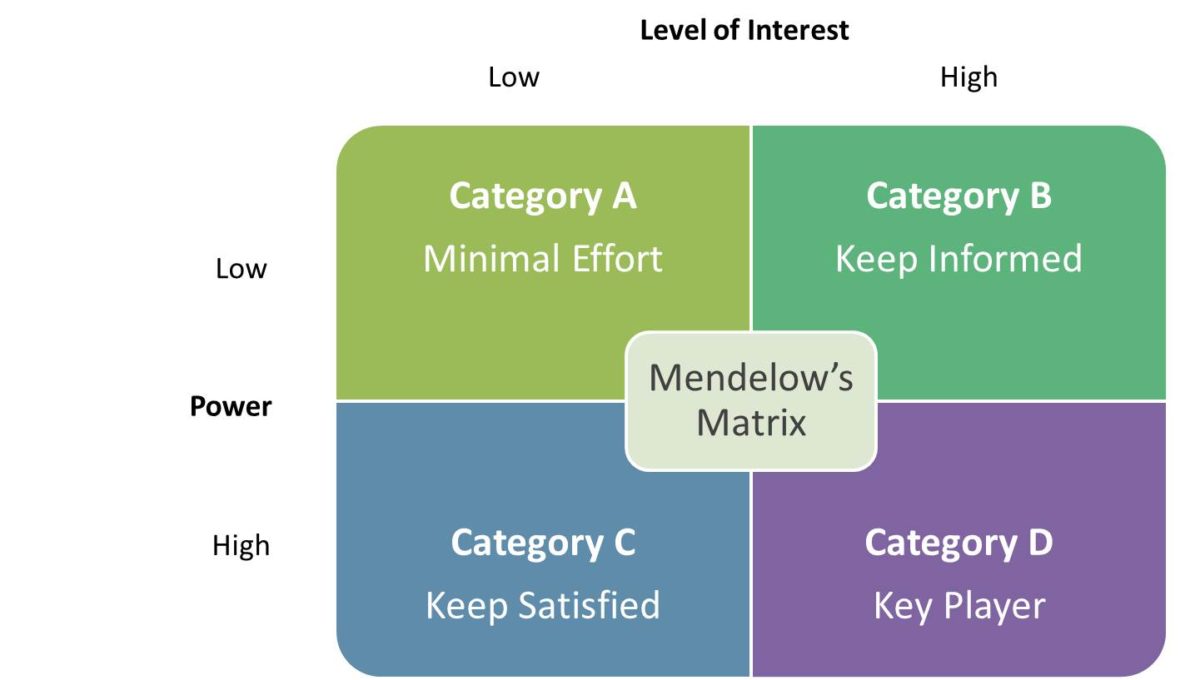
Source of diagram: https://www.mbaknol.com/strategic-management/stakeholder-analysis-mendelows-matrix/
Collection Process Organizing
Before the meeting with the stakeholders it is necessary to clarify:
- Types of communication (verbal or writing).
- Degree of formality.
- Frequency.
- Accountability.
- Location.
- Timezone.
- Cultural specifics.
- Other important conditions.
Read also: ‘Waterfall’ Model in IT Healthcare: Terms and Niches of Implementation
Sending a meeting minutes after every communication will be a good and useful habit. Also, scheduled communication should include information about the priority of issues to discuss, terms with dates and responsible teams.
When communicating — write everything down!
RACI-matrix is a simple and clear tool that helps to display the role and level of responsibility of all teams in context of certain phases or/and epic tasks of a project.
The abbreviation means the following:
R - Responsible for development or implementation
A - Accountable is the only role of the task (stage). Accountable is a team who has personal responsibility for the decision.
C - Consulted. Kind of specialist among stakeholders who gives any kind of additional information to understand the details of the requirements.
I - Informed teams don't have influence but need to keep up.
Sample of RACI-matrix
|
Tasks/Team |
Investor |
Product Owner |
PM |
BA |
Architector |
Tech Lead |
Designer |
|
Modules structure of the system |
I |
C |
R |
R |
A |
C |
I |
|
Mockup of the screens |
I |
A |
C |
C |
C |
R |
R |
|
Payment module connection |
I |
I |
A |
R |
R |
R |
I |
Read also: Use Case: Theoretical Definition And Practical Approach
Popular Techniques of Requirements Elicitation
Interview
This is the most common technique used to elicit requirements. Interview techniques should be used to build strong relationships between business analysts and stakeholders. In this technique, the interviewer directs questions to interested parties to obtain information. Individual interview is the most frequently used technique.
If the interviewer has a predetermined set of questions, it is called a structured interview which is more productive and prioritized
At repeat meetings Business Analyst's ready-made solutions enable the interviewee to quickly decide on a solution. In this case closed-ended questions can be answered in the form of "Yes" or "No", as well as for areas used to obtain confirmation of answers.
Read also: What ‘Scope Creep’ is and How to Escape It
Observation
The main purpose of an observation session is to understand the activities, tasks, tools used and events performed by others.
An observation plan ensures that all stakeholders know the purpose of the observation session, that they agree on the expected outcomes, and that the session meets their expectations. You need to inform participants that their performance is not being evaluated.
During the session, the observer should record all the actions and the time required to perform the work by others so that he/she can imitate the same. After the session, BA will review the results and continue working with the participants. Observation can be both active and passive.
Active observation is about asking questions and trying to sample the work that other people are doing.
Passive observation is silent observation, meaning you sit with others and simply watch them do their work without interpreting them.
Brainstorming
Kind of special form of meeting between project participants and interested parties from the customer’s side, dedicated to discussing those questions that cannot be answered as a result of ordinary interviews and which require the involvement of more people than just ‘user-analyst’ pairs.
This technique is used to generate new ideas and find a solution to a specific issue. Brainstorming members should be domain experts, subject matter specialists. Multiple ideas and information give you a storehouse of knowledge and you can choose from different ideas.
This session is usually conducted around the table. All participants should be given an equal amount of time to express their ideas. Creative thinking is the result of a brainstorming session that brings many ideas in a short time..
Scenarios
Context for collecting user requirements that defines answers to “what if” and “how is it done” questions regarding business processes implemented by users.
Prototypes
The great tool for refining and/or detailing requirements. There are different approaches to prototyping — from ‘paper’ models to pilot subsystems implemented as independent (in terms of resource management) projects or beta versions of products. Often prototypes are gradually transformed into project deliverables and used to validate and validate requirements
Analysis and review of documents
This technique is used to collect business information by reviewing and studying existing materials describing the business environment and process. This analysis is useful for validating the implementation of current solutions, as well as for understanding business needs.
Conclusion
Requirements elicitation is one of the the primary process of BA artifact collection with further preparation of software requirement specification for IT developments.
Process of requirements elicitation should be strongly organized with terms, members and prospective goals.
Process of requirements elicitation which was collected by brainstorming or interview, prototyping and other methods doesn’t give BA final decision as for requirements clarifying and its development. It’s some kind of scope of information which needs to be analyzed, systemized, and prioritized by the project management team into SRS, epics and tasks of IT project.
Software Development Hub is a reliable partner in providing outsourcing software development services for startups and existing products. Our team of experts is always focused on creating a quality product that will effectively solve your specific tasks.
If you are thinking of developing custom software you can ask us for help and project evaluation. We will assist you with market analysis and determining the relevance of development. Also, you will be able to take an active part in the development process of the solution, because good communication and adherence to your wishes are among our key priorities.
Our portfolio includes medical information systems, e-Prescription systems, applications for tracking medicines with a QR scanner, medical ERP systems, etc.
Categories
Share
Need a project estimate?
Drop us a line, and we provide you with a qualified consultation.