Lean Startup Methodology Cycle: 4 Steps to Risk-Free Success
Over the span of the last few years, the Lean Startup methodology has emerged as a highly sought-after approach among those embarking on the journey of establishing new ventures. These principled guidelines help entrepreneurs minimize risks while trying to introduce their products into the market. This serves as a practical response to the overwhelming risk involved in establishing and promoting a product in the market nowadays.
The lean startup methodology is explicitly crafted to create an environment that allows startups to have successful launches while minimizing risks, or at least mitigate them to an extent. Hence in this case, the startup runs a little chance of failure which is not only a good thing but also something that’s achievable within the confines of this model.
What contributes to the immense popularity of this particular technique? Research demonstrates that approximately 90% of new projects, regardless of their quality, prove unsuccessful, and die out within a mere year since their launch. This alarming truth is particularly alarming for small and medium enterprises as even if a large corporation fails it might as well manage losses from other ventures and continue its operations. However, for small start-ups operating on a tight budget, the collapse of any of their projects means an end to their business. Hence, it becomes imperative for them not just to measure down the maximum risks but also ensure that they maintain footing while in business. In this article, we will describe the key aspects of the lean startup methodology and its various stages.
What is the Lean Startup Methodology?
This technique was originally detailed in detail by Eric Ries in his book The Lean Startup. The concept drew inspiration from Toyota's lean production model which is centered on waste reduction and efficient resource allocation. The author notes that when the efforts, time, and money are wasted on an idea which, in the beginning, has failed for good; then not only does this have negative implications for a startup as such, at least in the beginning stages, but it also puts a lot of pressure on the entrepreneurs and supporters of the ideas.
Essentially, the road map for a startup activity comes with one important peculiarity in contrast to traditional lines of entrepreneurial activity, the one calls for a fully unexplored business model to commence operations. Research shows that for established lines of businesses adhering to a defined pattern is usually adequate to achieve success; in the case of the startup, the position is that its essence is to validate a certain assumption or idea. This means that the most crucial step in solidifying the nature of a startup is isolating a hypothesis within the context of that particular startup and testing its validity through experimentation. This method is better known as; testing the hypothesi; and it involves gauging customer feedback as well as establishing whether or not to stick to a given direction or to find a new one.
To summarize, the Lean Startup approach puts the emphasis on building services and products that real customers are interested in instead of constructing something that the founder believes might be necessary. The entire knowledge validation process offers an innovative approach in which all those initial ideas and premises will be scrutinized and put to the test to see what works and what does not.
Read also: Common Mistakes to Avoid when Building MVPThe 4 Steps of the Lean Startup Cycle
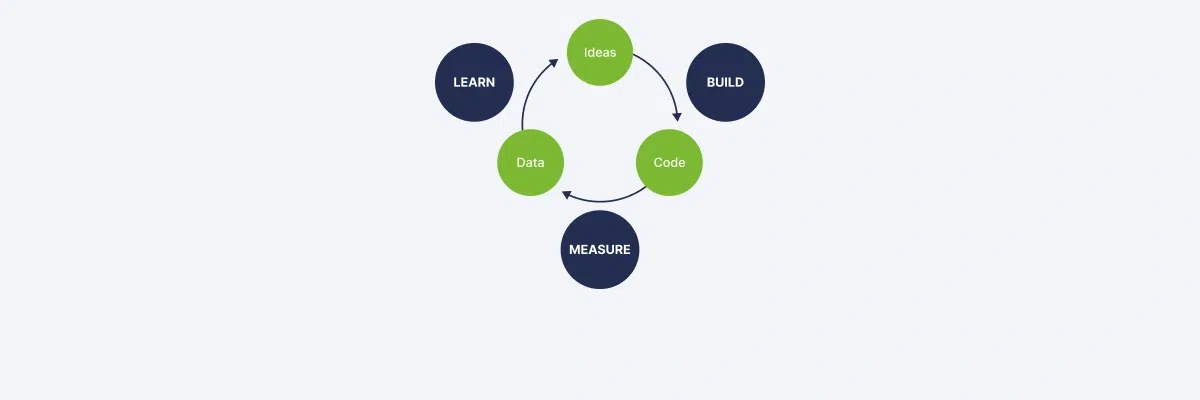
The methodology includes four required steps in its cyclical nature, which will be elaborated hereafter to show how things work in detail.
1. Business Model Template
- Customer segments: Who would be in need of your product? Who exactly is the type of client you would want to pursue?
- Value Proposition: What are the specific areas of pain you seek to address as a result of the implementation of this product? How does this product change customers' lives?
- Channels: Where will you get your clients? What method or medium do you want to employ in the communication process? What are the communication styles being employed by rival companies?
- Customer Relationships: Are you going for a completely automated and paperless engagement process? Are you headed for a more personalized, human-based approach?
- Revenue Streams: What options have you considered for making money? Do you have plans to provide a freemium version of the model? How would you describe the pricing model?
- Key Resources: What are the significant, specific resources essential in placing a value upon the customers? This could be an example of intellectual property. But is it possible to relate to the human capital?
- Key Activities: What essential activities, functions, or attributes one needs to possess in order to demonstrate a worthwhile proposition? What is the best way to build these relationships with clients?
- Key Partners: When looking into partnerships, what crucial partners or alliances does one need to have in relation to the USP? Is it necessary for the firm to engage into non-equity strategic alliances?
- Costs: What is the most financially costly of the entire list of resources, what models are most costly for the given business?
2. Hypothesis Formation
At this stage, the best player divides the hypotheses into three categories of risk, borrowed from the concept of design thinking. From most to least important, these categories are:
- Desirability;
- Viability;
- Feasibility.
3. Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
MVP is a variant of a new product through which information is collected with the least effort. By creating an MVP, you define/create for yourself:
- Product value;
- MVP type;
- Landing page;
- Explanatory video to introduce customers to the product.
4. Training
Software Development Services for Startups according to the lean cycle methodology completes the learning phase. In order for your product to meet market expectations, you must build customer feedback. This will help answer questions about:
- Saving or modifying an existing model;
- Adding/removing some features;
- The ability to charge for the use of the product;
- Choice of advertising model for business or freemium.
Software Development Hub is dedicated to creating applications for startups. Guided by the principles of modern development methodologies, we will help you determine the tasks and value of the product, draw up a work plan, etc. Enterprise software development services are performed using modern technologies and tools, which allow you to create a functioning product.
Our portfolio includes medical information systems, e-Prescription systems, applications for tracking medicines with a QR scanner, medical ERP systems, etc.
Categories
About the authors
Share
Need a project estimate?
Drop us a line, and we provide you with a qualified consultation.