Life Cycle of Healthcare Software: Regulations for the US Market
An effective process is significant in healthcare software development because of its mission and safety critical nature.
Product Life Cycle in Healthcare
Safe, secure, and reliable healthcare software shall be developed using a development process approved by a regulator. This is easily accomplished by providing compliance with a process standard, such as IEC 62304 for medical and healthcare industries. Other alternative standards typically exist within the relevant regulatory scope. The FDA, for instance, has process guidance in its set of regulatory instructions.
It is clear that quality, safety and reliability are decisive for the development of medical and healthcare systems. Appropriate quality standards from FDA, EMDD, IEC 62304, ISO 60601/61010 (safety and performance), ISO 14971 (risk management), ISO 13485 (quality management), IEC 62366 and other ISO/IEC/FDA standards require:
- full traceability of requirements through to product release;
- use of mature and transparent methods and processes;
- appropriate testing and risk management measures;
- comprehensive life cycle process documentation for compliance audits.
Basic Regulation Set
Adherence to relevant medical industry standards proves the safety and reliability of the products and can be a necessary precondition for market entry. The most important standard is IEC 62304 (Medical Device Software – Life Cycle Processes), which regulates and describes the development of software for medical and healthcare systems. The path to successful product development is cyclical and iterative, as any ideas are prototyped, tested, improved, retested, optimized, and refined.
According to the FDA, most of the overall healthcare product life cycle is in software development from concept to marketing. The path to successful device development is cyclical and iterative, as ideas are prototyped, tested, improved, retested, optimized and refined. The development pathway is a continuum with feedback loops and device modifications (Fig. 1).
Although it is presented as a split process with separate phases such as preclinical and clinical, the phases of product development overlap and parts may need to be repeated as testing and user experience are included into product changes and the device approaches its market form. In addition, product evaluations and modifications continue to occur even after the product goes to market. In the meantime, product evaluations and modifications continue to occur even after the product enters the marketplace.
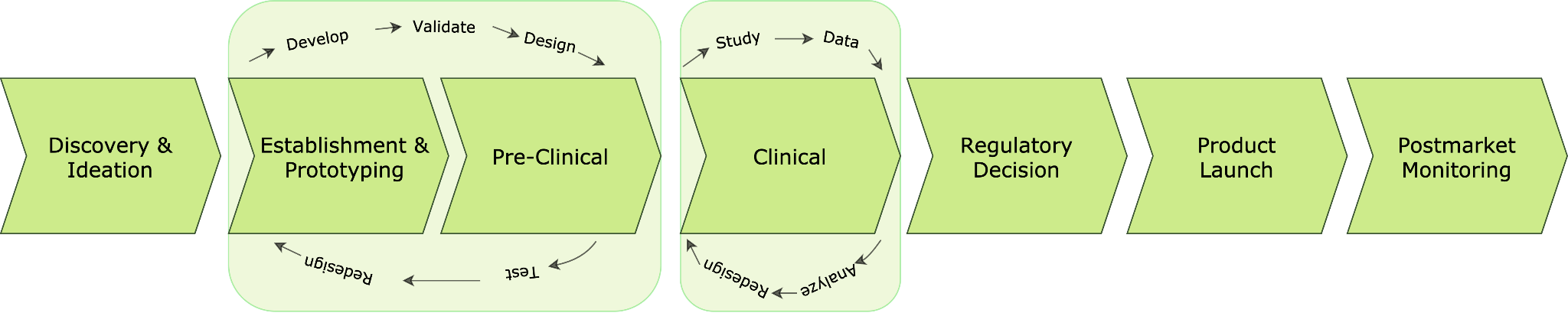
Fig. 1 - Healthcare products development path from discovery and idea to product launch and post-market monitoring according to FDA
The IEC 62304 specifications apply only to the personal embedded medical system’s component level and below. Validation is defined as “assessment of whether a product meets the requirements for the intended use” (IEC 60601-1) and “confirmation [...] that the requirements for a particular intended use or a particular intended application have been met” (ISO 13485/ISO 9001). That is, validation requires clearly defined expected use and valid use requirements. Test scenarios for the healthcare products as a whole must therefore cover all specifications for use in accordance with IEC 62366 and test all major tasks and all risk-related work steps. Insofar as IEC 62304 focuses on software embedded in medical devices, the requirements are formulated only for software verification, but not for validation. For this purpose, healthcare products manufacturers should refer to IEC 60601-1 or IEC 82304 (“Health Software”), which covers the top of the V model in the figure and also applies to so-called stand-alone software.
Medical Software Development Life Cycle
The IEC 62304 standard provides a life cycle process structure and requirements for each life cycle phase. The V model of software development is presented (Fig. 2) in accordance with this standard.
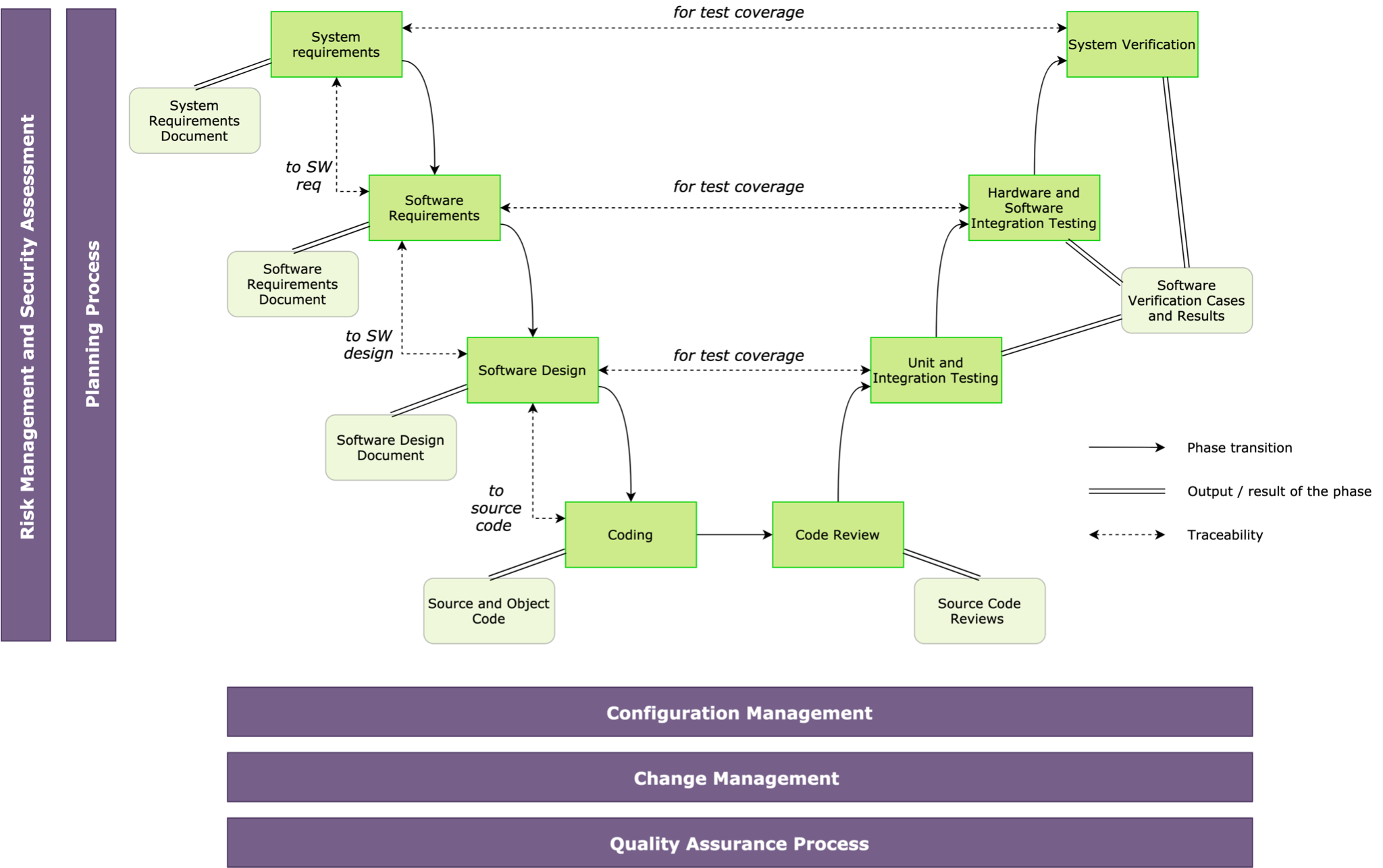
Fig. 2 – IEC 62304 Medical Software Life Cycle
The diagram depicts the healthcare software life cycle phases, outputs, links, and activities. The life cycle is defined by a planning process that uses an agreed set of plans and standards to describe actions and phases. The life cycle is supported by a configuration management process, a change management process, and software quality assurance. A major component of this life cycle is the risk and safety assessment actions that identify potential hazards and lead to the determination of the safety class of that component.
Read also: Requirements for Cybersecurity Ensuring of Healthcare IoT Systems
Traceability of Requirements
Software traceability is pivotal to the development of software for the healthcare industry and is required for regulatory approval. The US FDA CDRH “General Principles of Software Validation; Final Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff” document gives guidance on validation and traceability in healthcare products software development. The document's body of emphasizes that traceability is an important activity that provides support for reaching the final decision that the software has been validated.
Section 3.1.2 states “the validation of software typically includes evidence that all software requirements have been implemented correctly and completely and are traceable to system requirements”.
Section 3.2 specifies that “software validation includes confirmation of conformance to all software specifications and confirmation that all software requirements are traceable to the system specifications”. Section 5 of the document then emphasizes that traceability is a critical driver for almost all software development processes, especially with respect to requirements, design, construction, and testing processes.
Fig. 3 depicts a diagram for tracking healthcare products requirements at each stage of the software development life cycle and includes risk and change management.
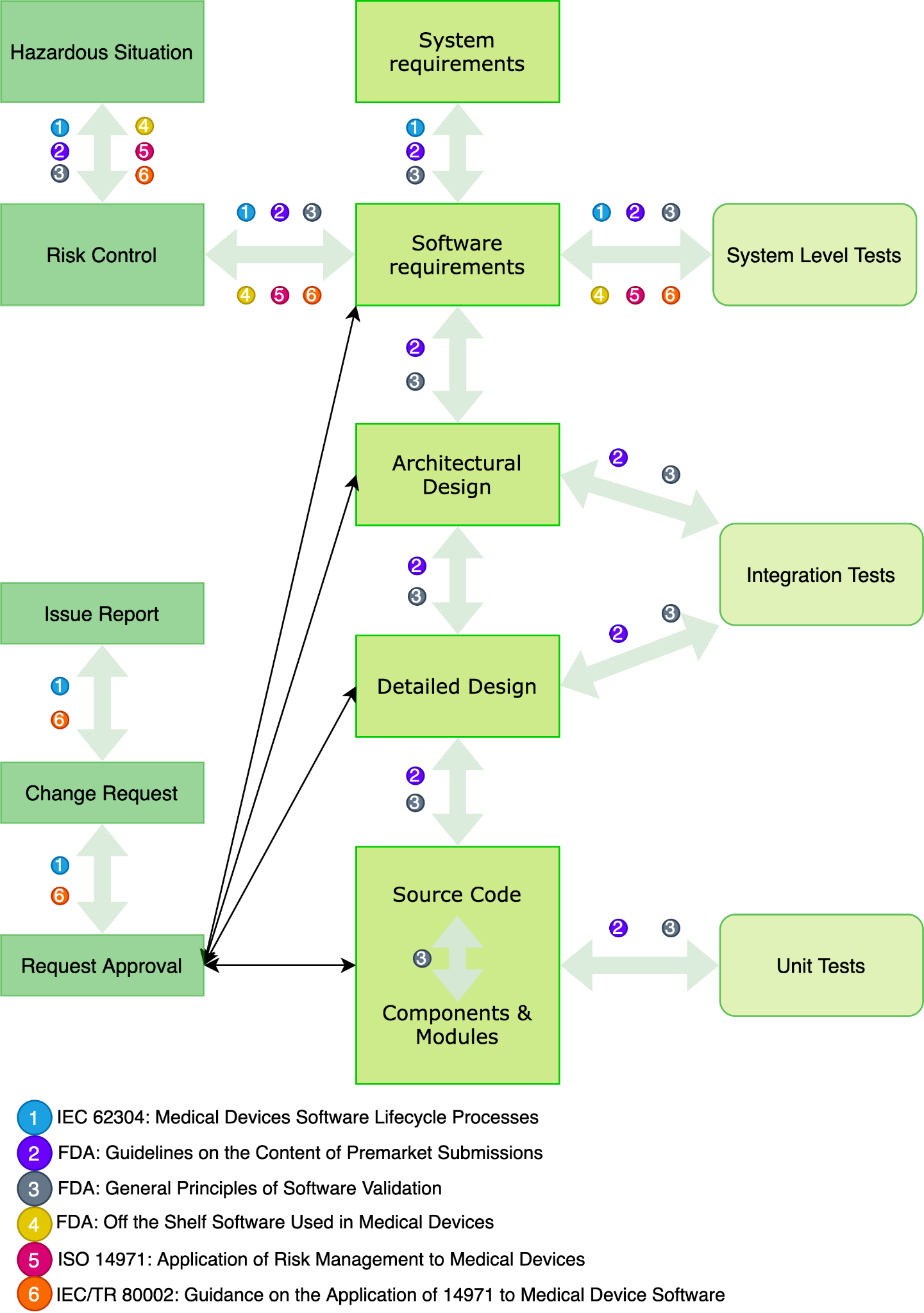
Fig. 3 – A diagram for traceability of healthcare products requirements
Conclusion
An effective process is significant in healthcare software development because of its mission and safety-critical nature. The requirements for the effective process are determined and mandated by a big number of industry standards, regulations, and guidelines. Failure to follow recommendations and guidelines will require backward-looking documentation generation and other actions, such as risk assessments or usability assessments, which can lead to unexpected design changes, software release delays, and commercial delays in getting to market.
Read also: 5 Healthcare Software Cybersecurity Breaches in 2022 in the U.S.
References
- IEC 62304. Medical Device Software - Software Life Cycle Processes.
- FDA: Appropriate Use of Voluntary Consensus Standards in Premarket Submissions for Medical Devices.
- IEC 60601. Medical electrical equipment. General requirements for basic safety and essential performance.
- ISO 14971. Medical devices -- Application of risk management to medical devices.
- ISO 13485. Medical devices -- Quality management systems -- Requirements for regulatory purposes.
- IEC 62366. Medical devices --Application of usability engineering to medical devices.
- IEC 82304. Health software.
- FDA: General Principles of Software Validation; Final Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff.
- Regan, G., Mc Caffery, F., Mc Daid, K., & Flood, D. (2013). Medical device standards’ requirements for traceability during the software development lifecycle and implementation of a traceability assessment model. Computer Standards & Interfaces, 36(1), pp. 3–9.
Categories
About the author
Share
Need a project estimate?
Drop us a line, and we provide you with a qualified consultation.