How to Write a Specification for IT Projects
The crucial role that a well-documented project specification plays in the success of IT projects is undeniable. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of creating a comprehensive project specification document, often referred to as a system requirements document (SRD) or product requirements document. We will also provide free templates to help streamline the process. Whether you're a seasoned project manager or new to the world of IT projects, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools needed to write an effective project specification.
What is a Project Specification?
A project specification, also known as a system requirements document, business or product requirements document, or project specification document, is a comprehensive outline of the goals, features, and technical requirements of an IT project. It serves as the foundation upon which the entire project is built, providing clear guidelines for both the development team and stakeholders.
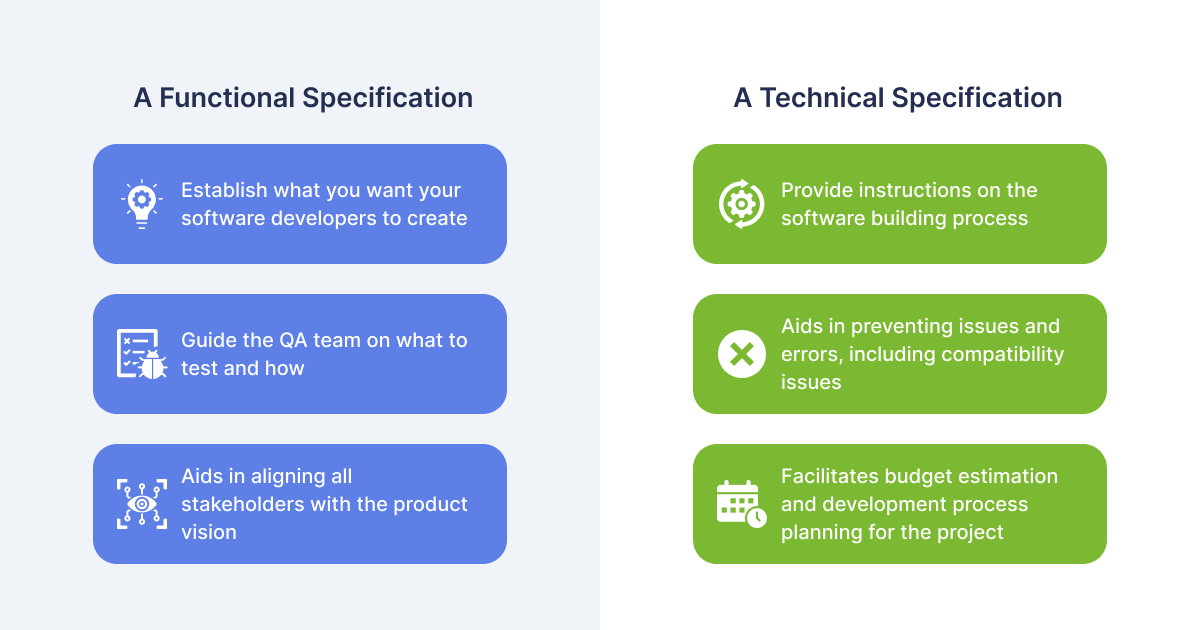
There are two types of design specifications:
- Functional - shows what capabilities are realized for the end user when interacting with a website or application. This is also called an open specification.
- A technical, or closed specification, describes the tools and technologies to achieve the objectives. If we imagine that the functional specification is the X icon on the map, then the technical specification is the route to reach the designated point.
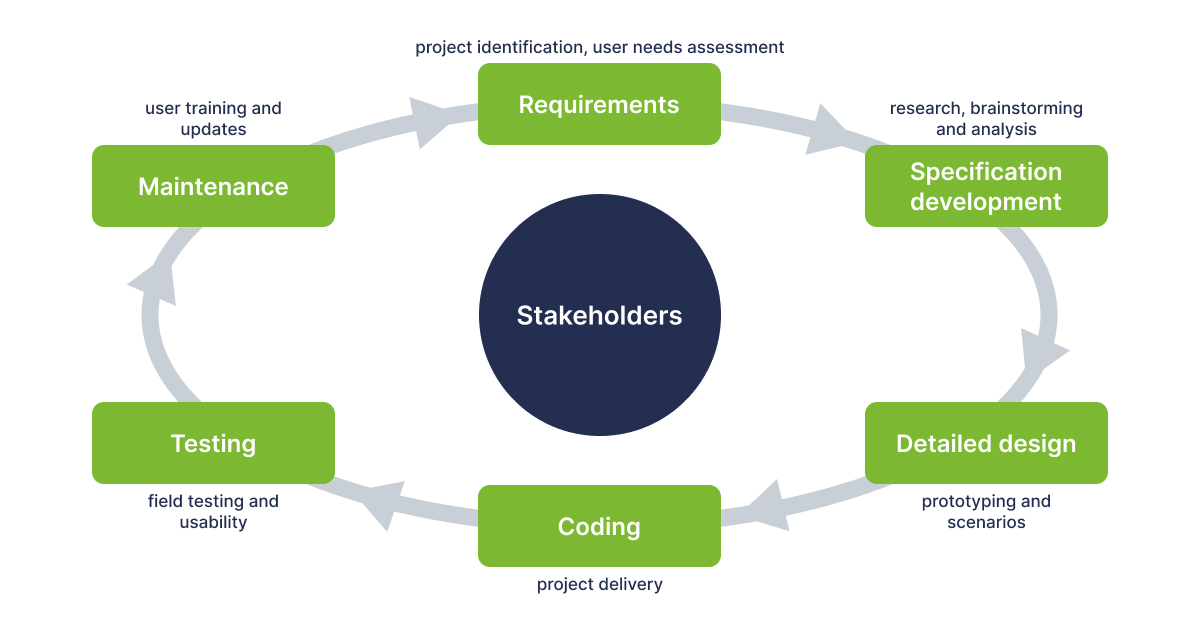
When Do You Need a Project Specification Document?
A project specification document is a necessity at the inception of any IT project. It is the roadmap that guides the project from concept to completion. Here are some key instances when you need a project specification.
Project Kickoff
Before you commence any development work, you need a clear project specification to ensure everyone is aligned on the project's objectives.
Scope Management
As the project progresses, the specification acts as a reference point to manage scope changes and ensure that the project stays on track.
Quality Assurance
It serves as a benchmark for quality assurance, allowing you to measure the project's progress against predefined criteria.
Communication Tool
It facilitates effective communication between stakeholders, developers, and testers, reducing misunderstandings and misinterpretations.
Legal Protection
In some cases, it can serve as a legal document that defines the obligations and responsibilities of each party involved in the project.
Typically, specifications are written early in the product development phase. For instance, the discovery phase of a project in an SDH company often involves the creation of a design specification.
What is a Technical Brief?
A technical brief, often prepared by a technical writer, is an essential component of the project specification. It provides in-depth technical details and explanations for developers and other technical stakeholders. The technical brief bridges the gap between the high-level project specification and the nitty-gritty technical aspects of the project. A technical brief usually implies the following steps:
- Create a list of all project participants, if known, from the principal stakeholder to the last cabin boy, including each person’s contact information.
- Outline each person’s role in creating the technical specs (technical writing, review, decision-making, approval, etc.).
- List all the tasks and subtasks to complete, indicating the name of the person responsible for the job (in a dedicated team, the PM performs this task).
- List all technologies that will be used in the project
Read also: Technical Documentation for IT Startups: Basic Types and Examples
What Information to Include in Your Project Specification
Brief Description of Your Company
Begin your project specification with a brief introduction to your company. Include information about your company's mission, vision, and values. This section helps set the context for the project and lets stakeholders understand your company's goals and objectives.
Description of Your Project
Provide a clear and concise description of your IT project. Explain the problem or need that the project aims to address. Outline the project's objectives and desired outcomes. Make sure to include any relevant background information that can help stakeholders understand the project's context.
Description of Your End-User Persona
Identify and describe your target audience or end-users. Create detailed user personas, including demographics, preferences, pain points, and goals. Understanding your end-users is crucial for tailoring the project to meet their needs effectively.
Your Unique Selling Points
Highlight what sets your project apart from the competition. Describe the unique features or benefits that make your project valuable. This section should clearly convey why your project is worth investing in.
Description of the Product's Functionalities
List and describe the key functionalities and features of the IT project. Use clear and concise language to explain what the project will do and how it will address the identified problem or need. Prioritize functionalities based on their importance and relevance.
How the Functionalities Will Be Implemented
Provide technical details on how each functionality will be implemented. This is where the technical brief comes into play. Discuss the technology stack, architecture, and development methodologies that will be used. Include diagrams or flowcharts if necessary to illustrate the technical aspects.
Defined Deadlines
Specify the project's timeline, including milestones and deadlines for each phase of development. A clear timeline ensures that everyone involved in the project is aware of the expected delivery dates and can plan accordingly.
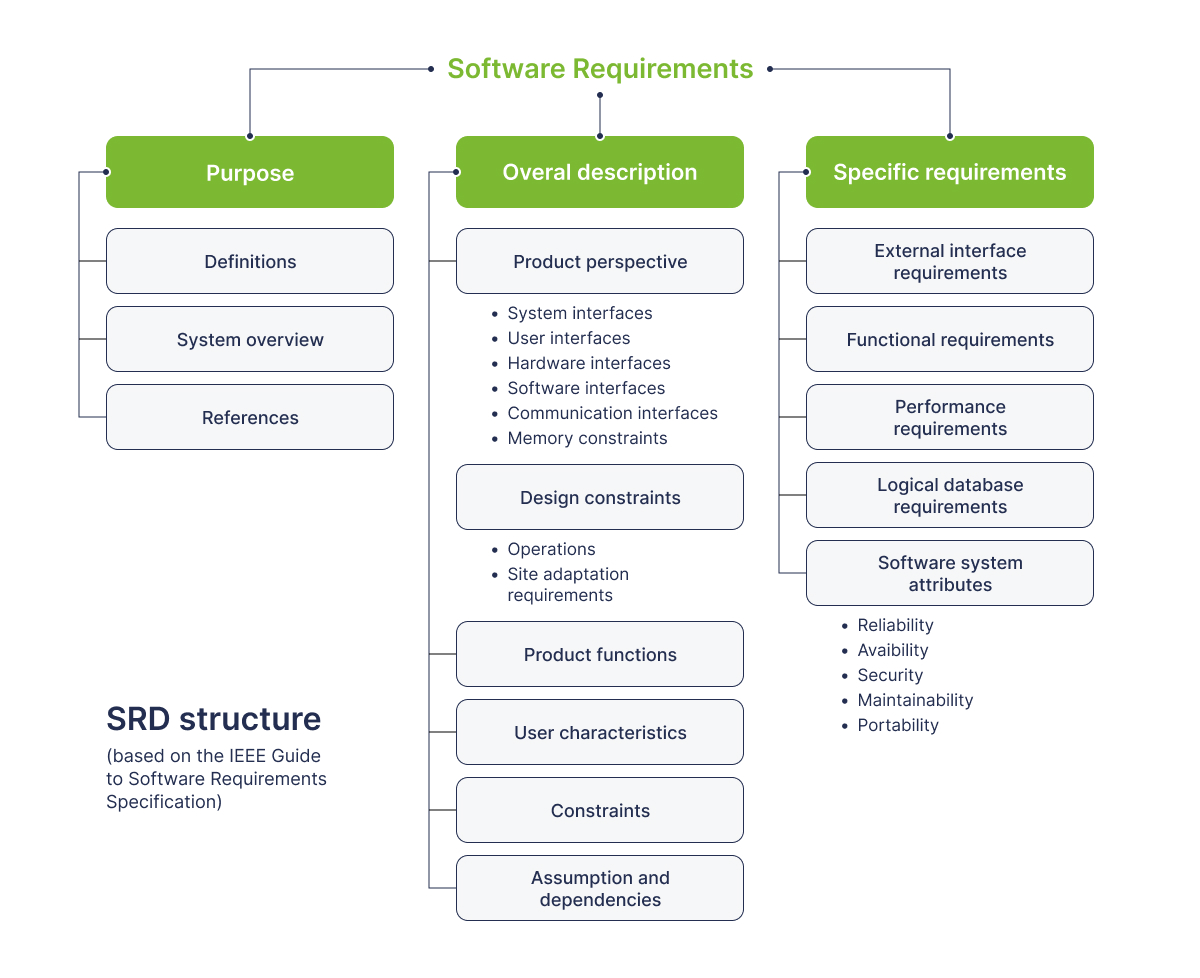
Your Project Budget Estimate
Include a budget estimate for the project. Break down the costs into categories such as development, testing, infrastructure, and any other relevant expenses. A well-defined budget helps in resource allocation and financial planning.
Read also: Software Requirements Specification and Its Key Components
How to Write a Specification for a Project
Now that we've covered the essential components, let's delve into the process of writing a project specification:
Gather Project Requirements from All Stakeholders
Begin by conducting thorough interviews and discussions with all project stakeholders. This includes executives, product managers, developers, testers, and end-users. Collect their input, expectations, and requirements for the project. Start with general project requirements for the product or its minimum viable product (MVP), then add more specific criteria.
Identify, List, and Analyze Your Functional Requirements
Based on the information gathered from stakeholders, identify and list the functional requirements of the project. Functional requirements describe what the system or software should do. These requirements should be detailed, specific, and testable.
Seek a Technical Writer's Help
For the technical aspects of your project specification, consider seeking the assistance of a technical writer or documentation specialist. A technical writer can help create a clear and detailed technical brief that explains how the project will be developed and implemented. This ensures that developers have a precise guide to follow, minimizing misunderstandings and errors during development.
In conclusion, a well-written project specification is the cornerstone of a successful IT project. It provides a clear roadmap, aligns stakeholders, and ensures that the project meets its objectives. By following the guidelines outlined in this article and using the provided templates, you can streamline the process of writing a project specification for your next IT project. Don't underestimate the power of a well-defined project specification; it can make the difference between project success and failure in the world of software development.
The company Software Development Hub works on IT projects, starting from the specification writing stage. To create a useful product adapted for monetization, we carefully study the goals, functions and capabilities of the application, taking into account the specifics of the customer’s activities. This allows you to achieve your goals and strengthen the competitiveness of your company.
Categories
Share
Need a project estimate?
Drop us a line, and we provide you with a qualified consultation.