HIPAA Compliance in Software Development
Personal health information is more exposed than ever in the digital age to theft, fraud, and unauthorised access. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) was approved in order to allay these worries and provide people more control over their medical information. HIPAA aims to increase the accessibility and continuity of health insurance coverage while establishing national standards for the privacy and security of personal health information.
Covered businesses and their associates are required to abide by a comprehensive set of rules and regulations in order to ensure compliance with HIPAA standards. In order to assure compliance with HIPAA standards, this article offers a summary of the law as well as a compliance checklist for covered companies and their business partners.
HIPAA Overview
In an increasingly digitised healthcare environment, privacy and security concerns around personal health information (PHI) led to the development of HIPAA. President Bill Clinton ratified the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act in 1996. Prior to HIPAA, there weren't many national regulations in place for the processing of PHI, and people had little control over how their health information was used and disclosed. Therefore, there have been cases of medical identity theft, fraud, and illegal access to PHI.
HIPAA set national standards for the privacy and security of PHI in addition to its main goals of enhancing the accessibility and continuity of health insurance coverage. By giving people the right to access their medical records and to decide how their health information is used and shared, HIPAA aims to provide patients more control over the information that relates to their health.
The use and disclosure of PHI by covered organisations, such as healthcare providers, health plans, and healthcare clearinghouses, is likewise governed by HIPAA regulations. PHI is safeguarded by these regulations from illegal access, use, or disclosure. HIPAA includes administrative simplification elements in addition to privacy and security provisions with the goal of enhancing the efficacy and efficiency of the healthcare system. These laws set guidelines for the use of electronic signatures as well as standards for transactions involving healthcare, such as the filing of claims and the determination of eligibility.
Essentially, HIPAA's key goals were to protect PHI's privacy and security, allow patients more control over their health information, and increase the effectiveness of the healthcare system by utilising electronic transactions. A significant step was taken in ensuring the security and integrity of personal health information in the United States with the creation and implementation of HIPAA.
Who must adhere to HIPAA regulations?
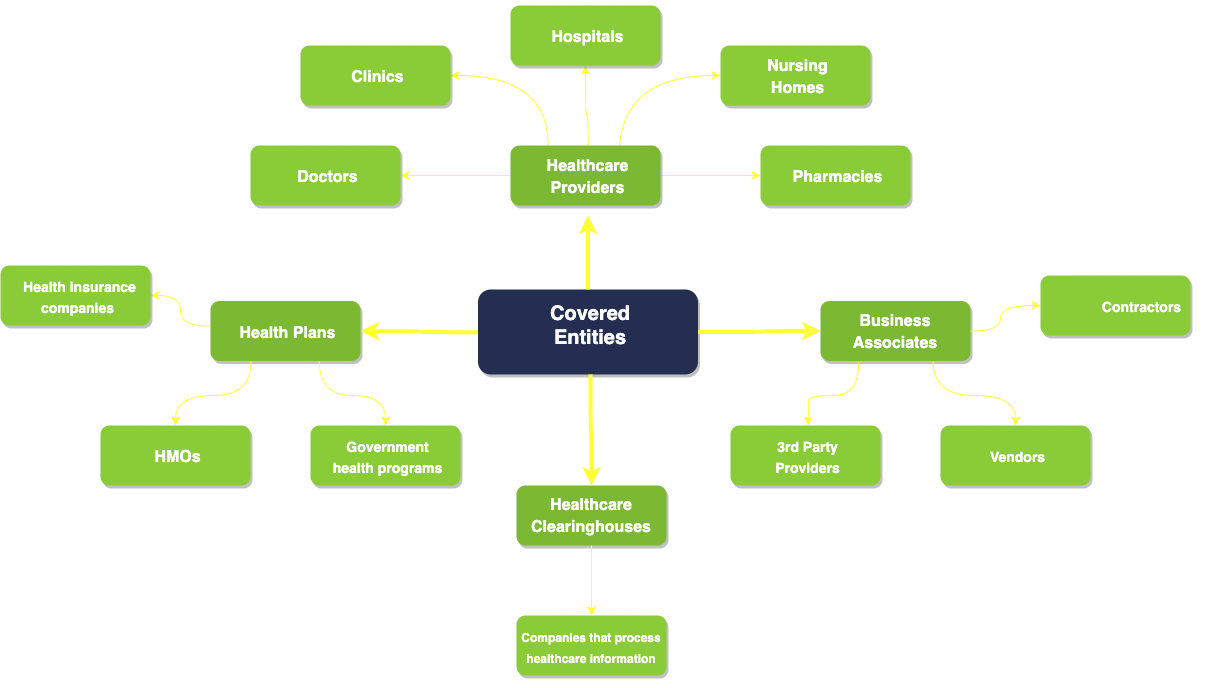
HIPAA Covered Entities
Covered organisations and their business associates are subject to HIPAA requirements. Health plans (health insurance companies, HMOs (Health Maintenance Organizations), and government health programs), healthcare clearinghouses (businesses that handle healthcare data for other organisations), and healthcare providers (doctors, clinics, hospitals, nursing homes, and pharmacies) are all examples of covered entities. Business associates are people or organisations that work with or on behalf of covered entities to offer services that may use or disclose PHI.
Hospitals, clinics, physicians, dentists, pharmacies, health insurance providers, and public healthcare initiatives are a few examples of covered enterprises. Business affiliates include entities that handle PHI for medical billing, transcribing services, and IT support.
It is significant to emphasise that people who manage their own health information, such as personal health records, and do not divulge it to covered businesses or business associates are not subject to HIPAA requirements.
The HIPAA Rules
The principal HIPAA rules that affect compliance are:
- Privacy Rule. This rule controls how covered companies and their business partners may use and disclose PHI. Patients are given the ability to access and manage their own PHI, and it establishes restrictions on how PHI may be used and released without patients' agreement.
- Security Rule. Under this rule, covered entities and business partners are required to put in place administrative, physical, and technical protections to secure the privacy, availability, and integrity of electronic PHI (ePHI).
- Breach Notification Rule. Under this regulation, whenever an unsecured PHI breach occurs, covered entities and business partners are required to inform impacted persons, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and, in certain circumstances, the media. There are two categories of breaches recognized under the HIPAA Breach Notification Rule: minor breaches and meaningful breaches. A PHI breach is considered minor if it affects fewer than 500 people. Covered organisations are expected to keep a log of the incident that contains details such as the date of the breach, the categories of PHI involved, the number of people affected, and the actions taken to lessen the harm. A PHI breach that has an impact on 500 people or more is considered to be meaningful. In this case, covered entities must inform anyone who may have been impacted, HHS, and the media, if appropriate, without undue delay but no later than 60 days from the time the breach was discovered. Moreover, covered businesses are required to give HHS a written notice that details the breach, the PHI categories implicated, the people affected, and the efforts taken to lessen the harm.
- Omnibus Rule. This rule amended HIPAA in a number of ways, notably by defining "business associates" to include subcontractors and mandating that both covered businesses and business associates abide by all HIPAA regulations.

HIPAA Penalty Structure (up-to beginning of 2023)
The HIPAA regulations have a considerable effect on compliance. The covered businesses and their business partners are required to take the necessary precautions to be in compliance with the regulations governing privacy, security, and breach reporting. HIPAA violations can lead to financial and criminal consequences as well as reputational harm for an entity. Hence, it is crucial that covered businesses and their business partners have the necessary policies, practices, and security measures in place to secure PHI and adhere to HIPAA.
Read also: HL7 Standard for Medical Applications
HIPAA Compliance Checklist
This is a HIPAA compliance checklist for businesses to use to confirm adherence to every requirement:
Privacy Rule:
- Establish rules and guidelines to protect PHI privacy.
- Designate a privacy officer to manage compliance with privacy laws.
- All employees should get training on privacy rules and practices.
- Before using or sharing patients' PHI for particular purposes, obtain written consent from them.
- Provide patients a notice of privacy practices outlining the organisation's privacy practices as well as their rights.
- Protect PHI by putting in place administrative, physical, and technological protections.
Security Rule:
- Put policies and processes in place that guarantee the availability, confidentiality, and integrity of electronic PHI (ePHI).
- To detect possible threats to ePHI, conduct a risk analysis and put the right security measures in place.
- Put administrative, physical, and technical measures in place to secure ePHI.
- A security officer should be appointed to manage security compliance.
- Provide security policies and procedures training to every employee.
Breach Notification Rule:
- Create rules and processes for handling a PHI breach.
- In the event that their PHI has been compromised, you must notify the persons impacted as soon as possible.
- If the breach affects more than 500 people, alert the Secretary of Health and Human Services.
- To ascertain the possibility of danger to persons, conduct a risk assessment, and then take the necessary precautions to prevent harm.
Omnibus Rule:
- Make that HIPAA regulations are followed by business partners.
- Get formal agreements that mandate HIPAA compliance from business partners.
- Provide patients more PHI privacy rights, such as the ability to limit certain disclosures.
- Observe the new guidelines for the use and sharing of PHI for marketing purposes.
It is worth noting that full compliance with the HIPAA rules is not limited to this checklist. Also to maintain continuing adherence to the HIPAA requirements, businesses should routinely evaluate and update their HIPAA compliance policies and processes.
Why is HIPAA compliance important for healthcare software developers?
Healthcare software developers are regarded as business associates under HIPAA if they build software that works with PHI. So, they are likewise required to adhere to HIPAA rules. Hence, building and putting into practice software that assures the privacy, security, and availability of PHI falls under the purview of healthcare software developers.
HIPAA mandates that administrative, physical, and technological security measures be put in place by healthcare software developers to ensure PHI.
Policies, practices, and training that are intended to control the selection, creation, application, and maintenance of the program are included in the administrative safeguards. Secure access controls, appropriate device storage, and correct disposal are just a few examples of the physical precautions. To guarantee that only those with permission may access PHI, technical measures include encryption, secure data transmission, and secure authentication.
Healthcare software developers should adhere to HIPAA regulations in order to preserve patient security and privacy. Non-compliance can cost a lot in terms of penalties, legal repercussions, and reputational harm for both the software developer and the healthcare provider. Furthermore, if patient information is not kept private and safe, it may undermine the trust and integrity of the healthcare sector as a whole.
In conclusion, preserving patient privacy, data security, and general compliance with HIPAA requirements all depend on IT healthcare system compliance. To stop unauthorised access, use, or disclosure of protected health information, a combination of administrative, physical, and technological measures must be in place. Although adopting HIPAAcompliance might be difficult, the dangers of non-compliance are high and can have serious repercussions, including penalties and legal actions. In order to achieve compliance, healthcare entities must thus take the essential actions, such as comprehending HIPAA requirements, identifying and managing risks, and putting best practices into effect. By doing this, they can guarantee that the health information of their patients is secured and that their healthcare practice complies with HIPAA requirements in full.
Software Development Hub has extensive experience in creating web applications and mobile applications for healthcare businesses. When working on a project, our team takes into account the business challenges the client faces and offers safe, efficient solutions to automate processes and scale your operations while reducing costs.
Categories
About the author
Share
Need a project estimate?
Drop us a line, and we provide you with a qualified consultation.








