IoT in Agriculture: Examples of Using Technologies for Smart Agro
The Internet of Things is rapidly penetrating most areas of human activity. Health and fitness apps, home automation solutions, automotive and logistics, smart city management systems, and the Industrial Internet of Things, - all work with connected devices.
Therefore, it is natural that the agricultural industry is also digitalized by IoT: the use of drones, and automation of routine operations can minimize human labor, and, thus, errors caused by the human factor. Gadgets and solutions for agriculture are an opportunity to control the process of crop and livestock production, optimize costs and increase efficiency. Given the constant growth of the world's population, the actualization of the issue of food, and, in general, the spread of technology in all areas of activity, the growth of the IoT market share in agriculture to more than $ 13 billion in 2022 is fully justified.
How is the Internet of Things used in agriculture? What are its advantages? We are going to tell you more below.
What is smart agriculture? Market definition and size
Speaking about smart agriculture, as a rule, they mean the use of IoT solutions in growing crops and animal husbandry. In other words, this is the use of IoT sensors for monitoring environmental and equipment indicators, which allows you to make the right decisions and increase productivity and efficiency of the industry.
For example, monitoring sensors allow you to determine the state of crops, and the number of pesticides and fertilizers needed to apply, which will give the desired harvest. In the same way, connected devices are used in smart farming.
The consumer sector has been remaining the leader in terms of IoT implementation. Nevertheless, indicators of IoT integration in agriculture are constantly growing, which is facilitated by modern realities. The COVID-19 pandemic has become an incentive for the development of smart agriculture: disrupted supply chains, and a shortage of qualified personnel have contributed to the increased introduction of connected gadgets to perform routine operations.
Moreover, the value of the smart farming market is expected to reach $15.3 billion in 2025. This creates unlimited opportunities for businesses that plan to implement technology solutions.
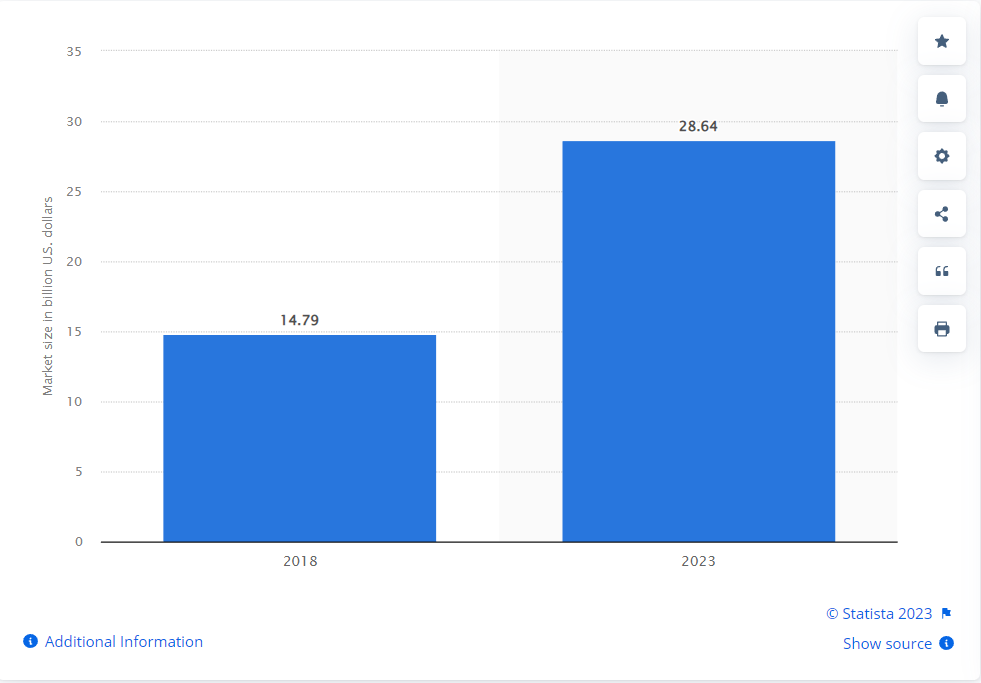
Global agricultural IoT market size in 2018 and 2023
Benefits of smart farming: how the Internet of Things affects agriculture
What are the advantages of an IoT solution for agriculture?

- Huge arrays of information collected through sensors will be used in the future to track the state and functioning of your business. Thus, data on the weather, the chemical composition of the soil, and the condition of cattle will allow you to make forecasts and make the right decisions, which in the future will positively affect the productivity of employees and the efficiency of the equipment.
- Control over internal operations is improved, which minimizes production risks. So, if you accurately predict the final volume of the products received, then the plans for its distribution will be more correct, which means that errors and the costs associated with them are leveled.
- Ability to effectively manage costs and reduce waste through performance control. If a crop failure or deterioration in the health of the livestock on the farm is foreseen, you are realistic in assessing the profit and can take action to eliminate the negative consequences.
- Process automation makes business work more efficient. Thus, the connected devices allow you to set up automated watering, fertilizing, and processing crops from pests.
- Product quality is improving, and production volumes are increasing due to strict control of production operations and automation.
- Reducing the negative impact on the environment.
With the right implementation and use of IoT solutions in agriculture, it is quite possible to increase income and scale business.

Examples of using IoT in agriculture
Farmers and agricultural business owners use a variety of sensors to work with the industry.
Monitoring of climatic conditions
Weather stations — these are the items you can most often find in automated enterprises in the field of animal husbandry and crop production. Such gadgets are distributed over land to collect information about the environment and form a map of climatic conditions, which is necessary for future planning.
Greenhouse automation
Monitoring of climatic conditions in greenhouses is a key to obtaining healthy crop in predictable volumes. IoT sensors provide real-time information about light, temperature, soil conditions and humidity levels in the greenhouse. In addition, such devices do not only collect data, but also correct conditions automatically.
Crop Management
Crop control devices are an important element of precision farming. They are also placed in fields to collect plant data. Gadgets analyze and transmit data on air temperature, rainfall, water potential of the leaves and even the state of the crop.
The staff of the enterprise can remotely monitor the growth of the crop, prevent the occurrence of abnormal phenomena and deal with crop diseases.
Cattle monitoring and management
Tracking the condition and behavior of animals is an important aspect of animal husbandry. Sensors connected to animals make it possible to monitor the health of livestock, mark their performance, identify sick individuals and separate them from the herd to avoid infection. Another element of monitoring is the use of drones, which replace personnel and have a number of advantages (greater productivity, objectivity, minimization of errors). One of the most common solutions is agricultural sensors on collars, through which the body temperature of cows, their state of health, the level of physical activity, the nature of nutrition, and the behavior of the herd as a whole are measured.
Precision farming
Precision farming works on the principle of making accurate decisions based on the information received. This application of IoT is also quite common in agriculture. So, with the help of IoT sensors, a huge pool of data is collected on various indicators of the field microclimate and ecosystem: illumination, soil and air temperature, chem. soil composition, moisture content, carbon dioxide saturation, and pest infestation. Based on such indicators, it is determined how much water, fertilizers, and pesticides are needed to reduce costs and obtain healthy crops.
One of the latest precision farming solutions is crop-specific temperature and conductivity measurement, which allows you to create detailed maps with information about soil areas and to maximize productivity.
Read also: How Internet of Things Makes Business Smarter
Predictive analytics for smart farming
Precision farming and predictive analysis are closely related. With real-time, up-to-date plant data, analytics help farmers predict harvest times, risks of disease, volume of harvest, etc. So you can manage the industry that is heavily dependent on weather and other factors beyond human control more effectively. For example, timely information about floods or droughts helps to adjust the supply of the required volumes of water and nutrients, save resources and reduce fertilizer losses.
Integrated farm management systems
Sophisticated farm performance management systems combine the work of several types of sensors with a control panel that is equipped with accounting, reporting, and analytics. Thus, the staff can monitor the operation of the farm remotely and optimize business processes on it. Additional options include logistics management, vehicle tracking, storage, etc.
Robots and autonomous machines
Automated agricultural machinery that works without human intervention allows you to cope with complex, repetitive tasks quickly and efficiently. These are, for example, automated tractors that work according to programmed routes and modes, robots for planting seeds / weeding / watering crops. Robots perform work efficiently, in accordance with strict requirements, relying on the mechanisms of computer vision and AI.
Software Development Hub is a company that has extensive experience in enterprise software development and IoT software development. We have a comprehensive approach to the implementation of projects, which allows our customers to scale their business and increase profits.
Categories
About the authors
Share
Need a project estimate?
Drop us a line, and we provide you with a qualified consultation.








