Gamification: Boosting User’s Engagement and Productivity
In IT products, gamification - the use of game-like aspects in non-game contexts - has become increasingly popular in recent years. IT businesses may engage and encourage users and enhance productivity and product-using satisfaction by introducing aspects of play and competition.
Users' motivation and engagement have been demonstrated to increase when using gamification in business processes. Companies may create a fun and exciting work atmosphere that motivates people to perform at their best by adding play, competition, and incentives. The most typical applications of gamification in business include the following:
- Task-based gamification: This entails presenting tasks that are similar to games to the user. A business may, for instance, give incentives for doing a specific number of tasks within a certain amount of time.
- Competition-based gamification: This entails setting up a hostile atmosphere where users compete with one another to accomplish particular objectives. This may be accomplished via leaderboards, group challenges, and other game-like elements.
- Reward-based gamification. This rewards certain behaviors or actions. For instance, if a user completes a training course or meets a certain sales target, their employer may reward them with a gift card.
Gamification has a significant influence on user engagement and output. Users are more likely to be engaged and productive if their activities are more fun and gratifying. Gamification may also boost cooperation and teamwork among users by fostering a feeling of community and competitiveness.
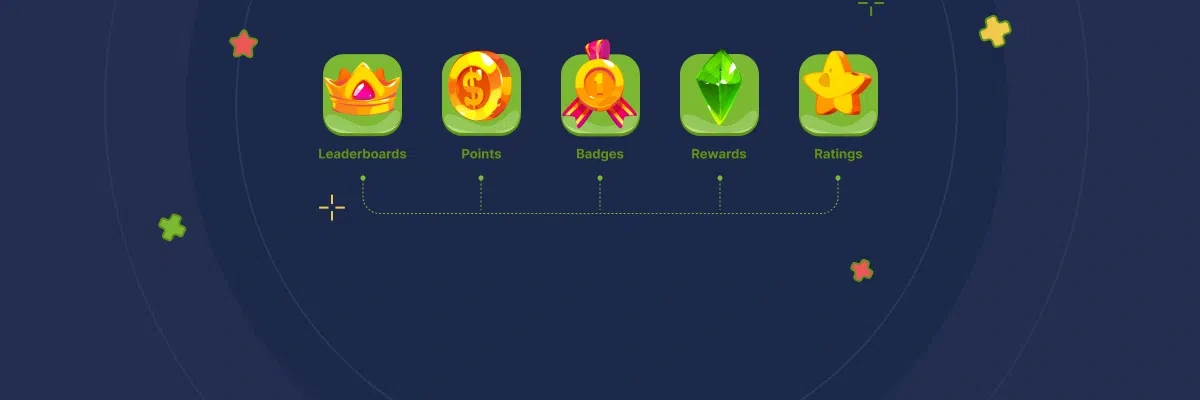
Elements of gamification
These elements tap into the psychological need for recognition, competition, and accomplishment, and can be used to encourage desired behaviors and actions in a business setting.
- Leaderboards: A leaderboard is a scoring system that shows participants' performance in a game or competition. Leaderboards are a useful tool in business gamification because they can be used to promote friendly rivalry and highlight those who are excelling at a particular job or activity.
- Points: In a game, players can acquire points as a form of currency. In business gamification, users can be rewarded with points for successfully performing activities, achieving goals, or making contributions to the company. A leaderboard's rankings can also be calculated using points to monitor progress.
- Badges: Badges are digital icons that stand in for accomplishments or significant reaches in a game or competition. Badges may be used in company gamification to recognize and honor staff for their efforts, commitment, and successes.
- Rewards: In a game, players may receive incentives in exchange for taking particular actions or achieving certain goals. In the context of business gamification, incentives may be utilized to encourage staff to perform well and accomplish their objectives. Gifts, bonuses, and promotions are examples of physical rewards, whereas prestige or recognition are examples of intangible ones.
- Ratings: Players or users can use ratings to assess the effectiveness or caliber of a certain item, service, or experience. Ratings can be used in business gamification to gauge consumer satisfaction, evaluate staff performance, or gauge the caliber of goods and services. Ratings may serve to provide a better knowledge of strengths and shortcomings and to highlight areas for improvement. They can be given by peers, managers, customers, or even an automated system. High ratings may also motivate users and serve as acknowledgment, and they may even be taken into account when determining promotions or performance reviews.
To make sure that the gamification elements support the business's objectives and are well-liked by users, customers, and workers, it's crucial to properly develop them, in which Software Development Hub already has a great expertise.
Principles of gamification
Business gamification refers to the use of game mechanics and design aspects to improve motivation, engagement, and performance in non-game situations. Some of the fundamental ideas of gamification include the ones listed below.
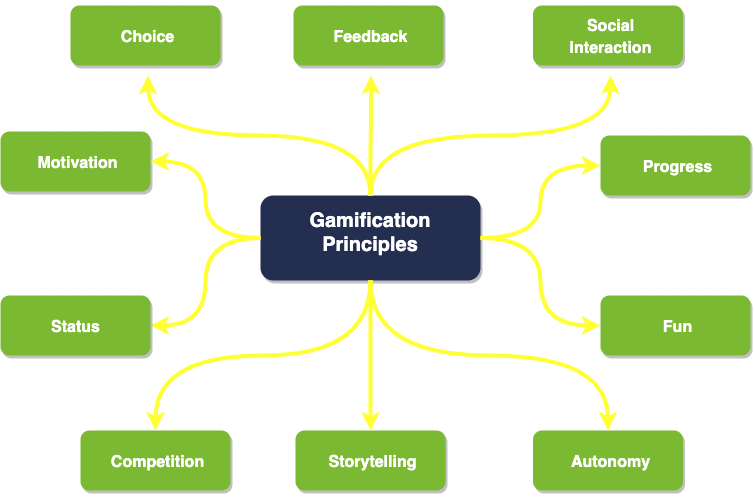
Key principles of business gamification
- Progress: Business gamification may keep people engaged and motivated to achieve their targets by giving them clear goals, benchmarks, and a sense of progress.
- Status: Gamification takes use of users' strong need for status and recognition by enabling them to get badges, ranks, and other types of honor for their accomplishments. This makes consumers feel like they are making progress and may motivate them to keep participating in the activity.
- Motivation: Gamification makes use of the intrinsic drivers that make games fun, such as the need to fulfill a task, the thrill of rivalry, and the sense of pride. Gamification may raise motivation and engagement by introducing these components into non-game activities.
- Feedback: Gamification gives users consistent, valuable feedback so they may observe their progress and learn from their failures. Because users feel in charge of their development and can see the results of their efforts, this promotes intrinsic motivation.
- Competition: Games frequently have competitive features like leaderboards and challenges, and business gamification employs this idea to instill a feeling of competition among users and motivate them to achieve greater levels of performance.
- Choice: Gamification frequently gives users options and choices that let them personalize their experiences, giving them a feeling of power and agency. Users may feel more motivated and engaged as a result since they have a sense of ownership over their progress and objectives.
- Autonomy: Since games frequently provide their users a sense of autonomy and control over their experiences, business gamification makes advantage of this idea by allowing users to choose how they want to play and engage with the game.
- Storytelling: Games frequently include an interesting narrative or tale, and business gamification employs this idea to create an engaging and immersive experience for users, keeping them engaged and encouraged to play.
- Social Incorporation: Gamification frequently includes social components, such as leaderboards, competition, and teamwork, that motivate users to interact with one another and assess their respective advancements. This could boost engagement and drive while fostering a feeling of community.
- Fun: To increase user involvement and make the experience memorable, business gamification should be engaging and entertaining.
The particular principles employed will depend on the precise aims and objectives of the gamification initiative. These are only a few of the basic pillars of business gamification.
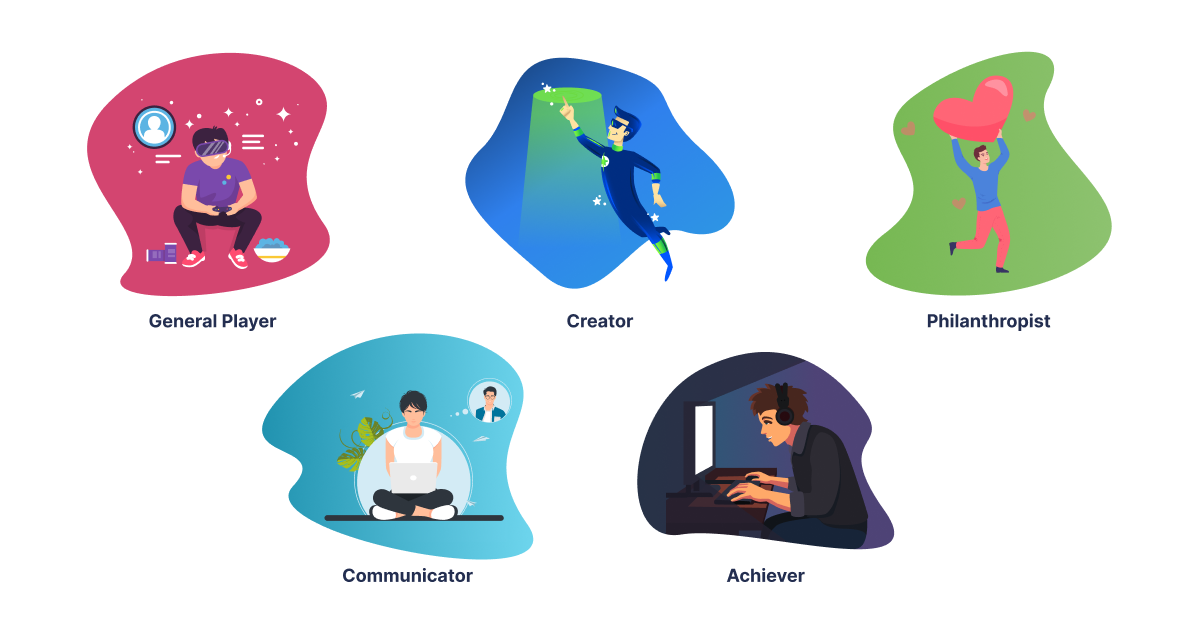
Target audience
Depending on the particular IT product and gamification strategy in question, the target audience of IT business gamification might vary significantly. But in a gamified system, the five sorts of players are frequently employed to classify people according to their goals and conduct:
- General Player: This kind of player is driven by the game's enjoyment and entertainment components. They want to take part in the game for the sake of sheer fun.
- Communicator: This sort of player is driven by interpersonal communication and social involvement. With friends, family, or coworkers, they like playing games and conversing about them.
- Creator: The chance to showcase their originality and uniqueness motivates this sort of gamer. They take pleasure in creating their own game pieces and modifying the gameplay.
- Achiever: This kind of gamer is inspired by the challenge of completing assignments and achieving objectives. They take pleasure in aiming for, earning, and being recognized for high scores.
- Philanthropist: This category of player is driven by the desire to help others and change the world for the better. They take pleasure in playing video games that let them change the world or support a cause.
Read also: Functional Decomposition: Aim, Procedure Description, Cases
Pitfalls of Gamification
Before applying gamification techniques, businesses should think about the following possible drawbacks of gamification:
- Demotivation: Some users may find gamification to be demotivating or perceive it as disrespecting their intelligence or abilities.
- Limited appeal: Not all users are driven by gaming-like experiences, therefore gamification may not work well for some groups or business domains.
- Overuse of gamification: While gamification may be a useful technique, overusing it might prevent product designers from being innovative and creative.
- Complexity: Putting a gamification approach into practice may be difficult and demanding in terms of technical know-how, time, and effort.
- Lack of sustainability: Gamification's exhilaration might be fleeting, and engagement levels could eventually drop off without regular updates and upgrades.
- Concerns regarding addiction: Gamification can encourage users to engage in addictive behaviors, which raises questions about how technology may affect mental health.
To conclude, gamification in the IT products is a powerful tool for boosting users' motivation and efficiency. Gamification may assist in establishing an atmosphere that motivates individuals to perform at their best, whether it's through task-based challenges, competition, or incentives. As little more than a consequence, businesses can experience more productivity, fulfillment at daily tasks, and general prosperity.
Software Development Hub provides services for writing mobile applications, web products and software for various fields. Competent implementation of client's ideas is possible due to expertise of technical specialists, whose work is coordinated by an experienced project manager.
Categories
About the author
Share
Need a project estimate?
Drop us a line, and we provide you with a qualified consultation.